Visceral fat area is a strong predictor of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2, a potential biomarker of dyslipidemia
- PMID: 28278265
- PMCID: PMC5344404
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173310
Visceral fat area is a strong predictor of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2, a potential biomarker of dyslipidemia
Abstract
Background: Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (LECT2) is a hepatokine linking obesity to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Although previous studies reported that obesity was associated with high levels of circulating LECT2 in human, the associations of detailed body fat distribution with LECT2 levels have not been examined. Furthermore, although animal study suggested that exercise decreased circulating LECT2 levels, it remains unknown whether physical fitness is associated with LECT2 levels in human. We therefore examined the relationship of plasma LECT2 levels with various adiposity indices and cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) in middle-aged and elderly Japanese men. Furthermore, we examined the relationship of LECT2 levels with the presence of metabolic syndrome, hypertension, insulin resistance and dyslipidemia to determine the clinical significance of measuring circulating LECT2.
Materials and methods: This was a cross-sectional study of 143 Japanese men (age: 30-79 years). Participants' plasma LECT2 levels were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. To assess their abdominal fat distributions, visceral fat area (VFA) and subcutaneous fat area (SFA) were measured using magnetic resonance imaging. CRF was assessed by measuring peak oxygen uptake ([Formula: see text]).
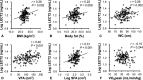
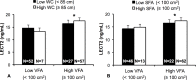
Results: All adiposity indices measured in this study were positively correlated with plasma LECT2 levels, while [Formula: see text] was negatively correlated with LECT2 levels after adjustment for age. The correlations, except for VFA were no longer significant with further adjustment for VFA. Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis revealed that VFA was the strongest predictor of plasma LECT2 levels. Plasma LECT2 levels differed based on the presence of metabolic syndrome and dyslipidemia, but not hypertension and insulin resistance. Logistic regression analyses revealed that plasma LECT2 levels were significantly associated with dyslipidemia independently of VFA; VFA was not significantly associated with dyslipidemia after adjustment for LECT2.
Conclusion: VFA was the strongest predictor of plasma LECT2 that is a potential biomarker linking visceral obesity to dyslipidemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatokine leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 as a biomarker of insulin resistance, liver enzymes, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in the general population.J Diabetes Investig. 2025 Feb;16(2):298-308. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14351. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Diabetes Investig. 2025. PMID: 39570764 Free PMC article.
-
Association of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (LECT2) with NAFLD, metabolic syndrome, and atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 4;12(4):e0174717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174717. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28376109 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationships between Metabolic Disorders (Hypertension, Dyslipidemia, and Impaired Glucose Tolerance) and Computed Tomography-Based Indices of Hepatic Steatosis or Visceral Fat Accumulation in Middle-Aged Japanese Men.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 3;11(3):e0149689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149689. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26938785 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular structure and role of LECT2 or CHM-II in arthritis, cancer, and other diseases.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jan;237(1):480-488. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30593. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34550600 Review.
-
[Bone metabolism in dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome].Clin Calcium. 2011 May;21(5):677-82. Clin Calcium. 2011. PMID: 21532116 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
LECT2: A pleiotropic and promising hepatokine, from bench to bedside.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(13):3598-3607. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17407. Epub 2022 Jun 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35656863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatokine leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 as a biomarker of insulin resistance, liver enzymes, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in the general population.J Diabetes Investig. 2025 Feb;16(2):298-308. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14351. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Diabetes Investig. 2025. PMID: 39570764 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Leukocyte Cell-Derived Chemotaxin-2 as a Risk Factor of Sarcopenia: Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 14;17(8):1342. doi: 10.3390/nu17081342. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40284206 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Intact and C-Terminal FGF23 with Inflammatory Markers in Older Patients Affected by Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 6;13(13):3967. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133967. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999530 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Biomarkers to Predict the Prognosis of Biliary Atresia by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 25;12:760182. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.760182. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34899846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1492(1):203–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

