Blood Ketones: Measurement, Interpretation, Limitations, and Utility in the Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- PMID: 28278308
- PMCID: PMC5734222
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2016.13.217
Blood Ketones: Measurement, Interpretation, Limitations, and Utility in the Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Abstract
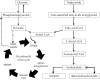
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) remains a common medical emergency. Over the last few years, new national guidelines have changed the focus in managing the condition from being glucose-centered to ketone-centered. With the advent of advancing technology and the increasing use of hand-held, point-of-care ketone meters, greater emphasis is placed on making treatment decisions based on these readings. Furthermore, recent warnings about euglycemic DKA occurring in people with diabetes using sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors urge clinicians to inform their patients of this condition and possible testing options. This review describes the reasons for a change in treating DKA, and outlines the benefits and limitations of using ketone readings, in particular highlighting the difference between urine and capillary readings.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reported no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Foster DW, McGarry JD. The metabolic derangements and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. N Eng J Med. 1983;309(3):159–169. - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD, Woeltje KF, Kuwajima M, Foster DW. Regulation of ketogenesis and the renaissance of carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989;5(3):271–284. - PubMed
-
- Stentz FB, Umpierrez GE, Cuervo R, Kitabchi AE. Proinflammatory cytokines, markers of cardiovascular risks, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation in patients with hyperglycemic crises. Diabetes. 2004;53(8):2079–2086. - PubMed
-
- Handelsman Y, Henry RR, Bloomgarden ZT, Dagogo-Jack S, DeFronzo RA, Einhorn D, Ferrannini E, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, Grunberger G. et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the association of SGLT-2 inhibitors and diabetic ketoacidosis. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(6):753–762. - PubMed
-
- Peters AL, Henry RR, Thakkar P, Tong C, Alba M. Diabetic ketoacidosis with canagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(4):532–538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
