Betacoronavirus Adaptation to Humans Involved Progressive Loss of Hemagglutinin-Esterase Lectin Activity
- PMID: 28279346
- PMCID: PMC7104930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.02.008
Betacoronavirus Adaptation to Humans Involved Progressive Loss of Hemagglutinin-Esterase Lectin Activity
Abstract
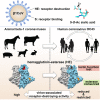
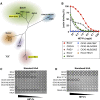
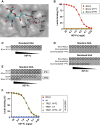
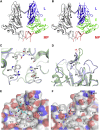
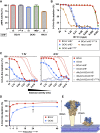
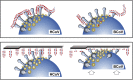
Human beta1-coronavirus (β1CoV) OC43 emerged relatively recently through a single zoonotic introduction. Like related animal β1CoVs, OC43 uses 9-O-acetylated sialic acid as receptor determinant. β1CoV receptor binding is typically controlled by attachment/fusion spike protein S and receptor-binding/receptor-destroying hemagglutinin-esterase protein HE. We show that following OC43's introduction into humans, HE-mediated receptor binding was selected against and ultimately lost through progressive accumulation of mutations in the HE lectin domain. Consequently, virion-associated receptor-destroying activity toward multivalent glycoconjugates was reduced and altered such that some clustered receptor populations are no longer cleaved. Loss of HE lectin function was also observed for another respiratory human coronavirus, HKU1. This thus appears to be an adaptation to the sialoglycome of the human respiratory tract and for replication in human airways. The findings suggest that the dynamics of virion-glycan interactions contribute to host tropism. Our observations are relevant also to other human respiratory viruses of zoonotic origin, particularly influenza A virus.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coronavirus hemagglutinin-esterase and spike proteins coevolve for functional balance and optimal virion avidity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 13;117(41):25759-25770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006299117. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32994342 Free PMC article.
-
Human Coronavirus HKU1 Spike Protein Uses O-Acetylated Sialic Acid as an Attachment Receptor Determinant and Employs Hemagglutinin-Esterase Protein as a Receptor-Destroying Enzyme.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(14):7202-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00854-15. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25926653 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evolutionary Adaptation toward Host Entry and Recognition of Receptor O-Acetyl Sialylation in Virus-Host Interaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 26;21(12):4549. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124549. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32604730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The acetyl-esterase activity of the hemagglutinin-esterase protein of human coronavirus OC43 strongly enhances the production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3097-107. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02699-12. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23283955 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and evolution of the hemagglutinin-esterase proteins of corona- and toroviruses.Glycoconj J. 2006 Feb;23(1-2):59-72. doi: 10.1007/s10719-006-5438-8. Glycoconj J. 2006. PMID: 16575523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Glycan-Binding Trait of the Sarbecovirus Spike N-Terminal Domain Reveals an Evolutionary Footprint.J Virol. 2022 Aug 10;96(15):e0095822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00958-22. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35852351 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19: should they be used as standard therapy?Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Aug;39(8):2461-2465. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05202-4. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32495226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for human coronavirus attachment to sialic acid receptors.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;26(6):481-489. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0233-y. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31160783 Free PMC article.
-
Kallikrein 13 serves as a priming protease during infection by the human coronavirus HKU1.Sci Signal. 2020 Nov 24;13(659):eaba9902. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aba9902. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 33234691 Free PMC article.
-
Coronaviruses and the central nervous system.J Neurovirol. 2020 Aug;26(4):459-473. doi: 10.1007/s13365-020-00868-7. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Neurovirol. 2020. PMID: 32737861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Groot R.J., Baker S.C., Baric R., Enjuanes L., Gorbalenya A.E., Holmes K.V., Perlman S., Poon L., Rottier P.J.M., Talbot P.J. Family Coronaviridae. In: King A., Lefkowitz E., Adams M.J., Carstens E.B., editors. Virus Taxonomy, Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Elsevier; 2011. pp. 806–828.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

