Lipidomic characterization and localization of phospholipids in the human lung
- PMID: 28280112
- PMCID: PMC5408611
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M074955
Lipidomic characterization and localization of phospholipids in the human lung
Abstract
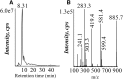
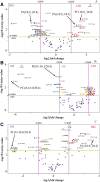
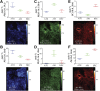
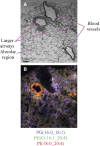
Lipids play a central role in lung physiology and pathology; however, a comprehensive lipidomic characterization of human pulmonary cells relevant to disease has not been performed. The cells involved in lung host defense, including alveolar macrophages (AMs), bronchial epithelial cells (BECs), and alveolar type II cells (ATIIs), were isolated from human subjects and lipidomic analysis by LC-MS and LC-MS/MS was performed. Additionally, pieces of lung tissue from the same donors were analyzed by MALDI imaging MS in order to determine lipid localization in the tissue. The unique distribution of phospholipids in ATIIs, BECs, and AMs from human subjects was accomplished by subjecting the large number of identified phospholipid molecular species to univariant statistical analysis. Specific MALDI images were generated based on the univariant statistical analysis data to reveal the location of specific cell types within the human lung slice. While the complex composition and function of the lipidome in various disease states is currently poorly understood, this method could be useful for the characterization of lipid alterations in pulmonary disease and may aid in a better understanding of disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: alveolar macrophages; alveolar type II cells; bronchial epithelial cells.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MALDI imaging MS of phospholipids in the mouse lung.J Lipid Res. 2011 Aug;52(8):1551-60. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M015750. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21508254 Free PMC article.
-
A mass spectrometry imaging and lipidomic investigation reveals aberrant lipid metabolism in the orthotopic mouse glioma.J Lipid Res. 2022 Dec;63(12):100304. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100304. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 36273646 Free PMC article.
-
Complementing Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Imaging with Chromatography Data for Improved Assignment of Isobaric and Isomeric Phospholipids Utilizing Trapped Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2021 Feb 2;93(4):2135-2143. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03942. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33416303
-
Phospholipids as cancer biomarkers: Mass spectrometry-based analysis.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018 Mar;37(2):107-138. doi: 10.1002/mas.21510. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018. PMID: 27276657 Review.
-
Enabling High Structural Specificity to Lipidomics by Coupling Photochemical Derivatization with Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Oct 19;54(20):3873-3882. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00419. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34570464 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid species profiling of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells of horses housed on two different bedding materials.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 8;13(1):21778. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49032-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38066223 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids in Equine Airway Inflammation: An Overview of Current Knowledge.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;14(12):1812. doi: 10.3390/ani14121812. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary toxicity of inhaled nano-sized cerium oxide aerosols in Sprague-Dawley rats.Nanotoxicology. 2019 Aug;13(6):733-750. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2018.1554751. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Nanotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30704321 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometric Imaging Reveals Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Bioactive Lipids in Arteries Undergoing Restenosis.J Proteome Res. 2019 Apr 5;18(4):1669-1678. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00941. Epub 2019 Mar 11. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30784274 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Omics-Scale Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Lipids in Brain Tissue Using a Multiclass Internal Standard Mixture.Anal Chem. 2023 Dec 26;95(51):18719-18730. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02724. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 38079536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S. E., Lindgren J. A., Rouzer C. A., and Serhan C. N.. 1987. Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 237: 1171–1176. - PubMed
-
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., and Soberman R. J.. 1990. Leukotrienes and other products of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Biochemistry and relation to pathobiology in human diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 323: 645–655. - PubMed
-
- Riccioni G., Bucciarelli T., Mancini B., Di Ilio C., and D’Orazio N.. 2007. Antileukotriene drugs: clinical application, effectiveness and safety. Curr. Med. Chem. 14: 1966–1977. - PubMed
-
- Drakatos P., Lykouras D., Sampsonas F., Karkoulias K., and Spiropoulos K.. 2009. Targeting leukotrienes for the treatment of COPD? Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets. 8: 297–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

