Metabolic fate of glucose and candidate signaling and excess-fuel detoxification pathways in pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 28280244
- PMCID: PMC5418042
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.763060
Metabolic fate of glucose and candidate signaling and excess-fuel detoxification pathways in pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
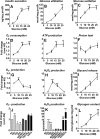
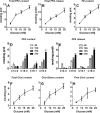
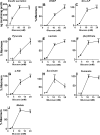
Glucose metabolism promotes insulin secretion in β-cells via metabolic coupling factors that are incompletely defined. Moreover, chronically elevated glucose causes β-cell dysfunction, but little is known about how cells handle excess fuels to avoid toxicity. Here we sought to determine which among the candidate pathways and coupling factors best correlates with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), define the fate of glucose in the β-cell, and identify pathways possibly involved in excess-fuel detoxification. We exposed isolated rat islets for 1 h to increasing glucose concentrations and measured various pathways and metabolites. Glucose oxidation, oxygen consumption, and ATP production correlated well with GSIS and saturated at 16 mm glucose. However, glucose utilization, glycerol release, triglyceride and glycogen contents, free fatty acid (FFA) content and release, and cholesterol and cholesterol esters increased linearly up to 25 mm glucose. Besides being oxidized, glucose was mainly metabolized via glycerol production and release and lipid synthesis (particularly FFA, triglycerides, and cholesterol), whereas glycogen production was comparatively low. Using targeted metabolomics in INS-1(832/13) cells, we found that several metabolites correlated well with GSIS, in particular some Krebs cycle intermediates, malonyl-CoA, and lower ADP levels. Glucose dose-dependently increased the dihydroxyacetone phosphate/glycerol 3-phosphate ratio in INS-1(832/13) cells, indicating a more oxidized state of NAD in the cytosol upon glucose stimulation. Overall, the data support a role for accelerated oxidative mitochondrial metabolism, anaplerosis, and malonyl-CoA/lipid signaling in β-cell metabolic signaling and suggest that a decrease in ADP levels is important in GSIS. The results also suggest that excess-fuel detoxification pathways in β-cells possibly comprise glycerol and FFA formation and release extracellularly and the diversion of glucose carbons to triglycerides and cholesterol esters.
Keywords: glucodetoxification; glucose metabolism; insulin secretion; lipid metabolism; metabolomics; mitochondrial metabolism; pancreatic β cells.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
-
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M., and Madiraju S. R. (2013) Metabolic signaling in fuel-induced insulin secretion. Cell Metab. 18, 162–185 - PubMed
-
- Henquin J. C. (2011) The dual control of insulin secretion by glucose involves triggering and amplifying pathways in β-cells. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 93, Suppl. 1, S27–S31 - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Bryan L., Nichols C. G., Wechsler S. W., Clement J. P. 4th, Boyd A. E. 3rd, González G., Herrera-Sosa H., Nguy K., Bryan J., and Nelson D. A. (1995) Cloning of the β cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science 268, 423–426 - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., and Ashcroft S. J. (1984) Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic β-cells. Nature 312, 446–448 - PubMed
-
- Straub S. G., and Sharp G. W. (2002) Glucose-stimulated signaling pathways in biphasic insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 18, 451–463 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

