Umeclidinium/vilanterol as step-up therapy from tiotropium in patients with moderate COPD: a randomized, parallel-group, 12-week study
- PMID: 28280319
- PMCID: PMC5338844
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S119032
Umeclidinium/vilanterol as step-up therapy from tiotropium in patients with moderate COPD: a randomized, parallel-group, 12-week study
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with COPD who remain symptomatic on long-acting bronchodilator monotherapy may benefit from step-up therapy to a long-acting bronchodilator combination. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of umeclidinium (UMEC)/vilanterol (VI) in patients with moderate COPD who remained symptomatic on tiotropium (TIO).
Methods: In this randomized, blinded, double-dummy, parallel-group study (NCT01899742), patients (N=494) who were prescribed TIO for ≥3 months at screening (forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1]: 50%-70% of predicted; modified Medical Research Council [mMRC] score ≥1) and completed a 4-week run-in with TIO were randomized to UMEC/VI 62.5/25 µg or TIO 18 µg for 12 weeks. Efficacy assessments included trough FEV1 at Day 85 (primary end point), 0-3 h serial FEV1, rescue medication use, Transition Dyspnea Index (TDI), St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), and COPD Assessment Test (CAT). Safety evaluations included adverse events (AEs).
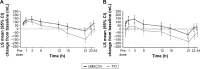
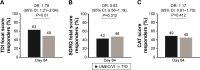
Results: Compared with TIO, UMEC/VI produced greater improvements in trough FEV1 (least squares [LS] mean difference: 88 mL at Day 85 [95% confidence interval {CI}: 45-131]; P<0.001) and FEV1 after 5 min on Day 1 (50 mL [95% CI: 27-72]; P<0.001). Reductions in rescue medication use over 12 weeks were greater with UMEC/VI versus TIO (LS mean change: -0.1 puffs/d [95% CI: -0.2-0.0]; P≤0.05). More patients achieved clinically meaningful improvements in TDI score (≥1 unit) with UMEC/VI (63%) versus TIO (49%; odds ratio at Day 84=1.78 [95% CI: 1.21-2.64]; P≤0.01). Improvements in SGRQ and CAT scores were similar between treatments. The incidence of AEs was similar with UMEC/VI (30%) and TIO (31%).
Conclusion: UMEC/VI step-up therapy provides clinical benefit over TIO monotherapy in patients with moderate COPD who are symptomatic on TIO alone.
Keywords: COPD; LABA; LAMA; step-up; tiotropium; umeclidinium/vilanterol.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure EMK has served on advisory boards, speaker panels, and received travel reimbursement from Amphastar, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Forest, Ironwood, Mylan, Novartis, Pearl, Sunovion, Targacept, Teva, and Theravance; has conducted multicenter clinical research trials for ~40 pharmaceutical companies. CJK, DVG, C-QZ, AC, JHR, and WAF are employees of GSK and hold stocks/shares in GSK. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative Efficacy of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Versus Other Bronchodilators for the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis.Adv Ther. 2022 Nov;39(11):4961-5010. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02234-x. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35857184 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy of umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 μg on health-related quality of life in patients with COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 May 9;11:971-9. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S102962. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 27274218 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dual Bronchodilator Therapy with Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Versus Tiotropium plus Indacaterol in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Drugs R D. 2016 Jun;16(2):217-27. doi: 10.1007/s40268-016-0131-2. Drugs R D. 2016. PMID: 27028749 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of rescue medication use and medication adherence receiving umeclidinium/vilanterol versus tiotropium bromide/olodaterol.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Sep 4;14:2047-2060. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S213520. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019. PMID: 31564852 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of comparative efficacy of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol versus other bronchodilators in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):609. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03445-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39696097 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Umeclidinium bromide versus placebo for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 20;6(6):CD011897. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011897.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28631387 Free PMC article.
-
Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Compared with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol, Budesonide/Formoterol, and Tiotropium as Initial Maintenance Therapy in Patients with COPD Who Have High Costs and Comorbidities.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Apr 22;16:1149-1161. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S298032. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 33911860 Free PMC article.
-
Open-Label, Crossover Study to Determine the Pharmacokinetics of Fluticasone Furoate and Batefenterol When Administered Alone, in Combination, or Concurrently.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2019 Feb;8(2):188-197. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.603. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2019. PMID: 30070770 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence-based review of data on the combination inhaler umeclidinium/vilanterol in patients with COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Jun 6;14:1251-1265. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S191845. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019. PMID: 31239659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol Versus Other Bronchodilators for the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis.Adv Ther. 2022 Nov;39(11):4961-5010. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02234-x. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35857184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GOLD [homepage on the Internet] Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2016. [Accessed January 4, 2017]. [cited July 25, 2016]. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.com/
-
- Blair HA, Deeks ED. Umeclidinium/vilanterol: a review of its use as maintenance therapy in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Drugs. 2015;75(1):61–74. - PubMed
-
- GSK ANORO™ ELLIPTA® [prescribing information] 2014. [Accessed September 2015]. Available from: https://www.gsksource.com/gskprm/htdocs/documents/ANORO-ELLIPTA-PI-MG.PDF.
-
- GSK [webpage on the Internet] ANORO™ ELLIPTA® summary of product characteristics. 2014. [Accessed September 2015]. Available from: http://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/28949#INDICATIONS.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

