Understanding Host-Pathogen Interactions with Expression Profiling of NILs Carrying Rice-Blast Resistance Pi9 Gene
- PMID: 28280498
- PMCID: PMC5322464
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00093
Understanding Host-Pathogen Interactions with Expression Profiling of NILs Carrying Rice-Blast Resistance Pi9 Gene
Abstract
Magnaporthe oryzae infection causes rice blast, a destructive disease that is responsible for considerable decrease in rice yield. Development of resistant varieties via introgressing resistance genes with marker-assisted breeding can eliminate pesticide use and minimize crop losses. Here, resistant near-isogenic line (NIL) of Pusa Basmati-1(PB1) carrying broad spectrum rice blast resistance gene Pi9 was used to investigate Pi9-mediated resistance response. Infected and uninfected resistant NIL and susceptible control line were subjected to RNA-Seq. With the exception of one gene (Pi9), transcriptional signatures between the two lines were alike, reflecting basal similarities in their profiles. Resistant and susceptible lines possessed 1043 (727 up-regulated and 316 down-regulated) and 568 (341 up-regulated and 227 down-regulated) unique and significant differentially expressed loci (SDEL), respectively. Pathway analysis revealed higher transcriptional activation of kinases, WRKY, MYB, and ERF transcription factors, JA-ET hormones, chitinases, glycosyl hydrolases, lipid biosynthesis, pathogenesis and secondary metabolism related genes in resistant NIL than susceptible line. Singular enrichment analysis demonstrated that blast resistant NIL is significantly enriched with genes for primary and secondary metabolism, response to biotic stimulus and transcriptional regulation. The co-expression network showed proteins of genes in response to biotic stimulus interacted in a manner unique to resistant NIL upon M. oryzae infection. These data suggest that Pi9 modulates genome-wide transcriptional regulation in resistant NIL but not in susceptible PB1. We successfully used transcriptome profiling to understand the molecular basis of Pi9-mediated resistance mechanisms, identified potential candidate genes involved in early pathogen response and revealed the sophisticated transcriptional reprogramming during rice-M. oryzae interactions.
Keywords: Magnaporthe oryzae; RNA-Seq; WRKY; ethylene; host-pathogen interaction; jasmonic acid; near isogenic lines; rice blast.
Figures


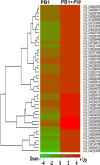

Similar articles
-
Deciphering signalling network in broad spectrum Near Isogenic Lines of rice resistant to Magnaporthe oryzae.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 15;9(1):16939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50990-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31729398 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines for major blast resistance gene(s) in Basmati rice.Theor Appl Genet. 2015 Jul;128(7):1243-59. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2502-4. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Theor Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25869921
-
Improving of Rice Blast Resistances in Japonica by Pyramiding Major R Genes.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 3;7:1918. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01918. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28096805 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular progress on the mapping and cloning of functional genes for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.): current status and future considerations.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016;36(2):353-67. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.961403. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 25394538 Review.
-
Understanding the Dynamics of Blast Resistance in Rice-Magnaporthe oryzae Interactions.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 May 30;8(6):584. doi: 10.3390/jof8060584. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Dynamics of Receptor-Based Genes Reveal Immunity Hubs in Rice Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 12;26(10):4618. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104618. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429762 Free PMC article.
-
Global transcriptome and coexpression network analyses reveal cultivar-specific molecular signatures associated with different rooting depth responses to drought stress in potato.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 19;13:1007866. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1007866. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340359 Free PMC article.
-
RiceMetaSysB: a database of blast and bacterial blight responsive genes in rice and its utilization in identifying key blast-resistant WRKY genes.Database (Oxford). 2019 Jan 1;2019:baz015. doi: 10.1093/database/baz015. Database (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30753479 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Coupled with a Critical-Time-Point Analysis during Pathogenesis for Predicting the Molecular Mechanism Underlying Blast Resistance in Rice.Rice (N Y). 2020 Dec 11;13(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12284-020-00439-8. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 33306159 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq analysis of gene expression changes triggered by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in a susceptible rice genotype.Rice (N Y). 2019 Jun 24;12(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0301-2. Rice (N Y). 2019. PMID: 31236783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akimoto-Tomiyama C., Sakata K., Yazaki J., Nakamura K., Fujii F., Shimbo K., et al. . (2003). Rice gene expression in response to N-acetylchitooligosaccharide elicitor, comprehensive analysis by DNA microarray with randomly selected ESTs. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 537–551. 10.1023/A:1024890601888 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bagnaresi P., Biselli C., Orrù L., Urso S., Crispino L., Abbruscato P., et al. . (2012). Comparative transcriptome profiling of the early response to Magnaporthe oryzae in durable resistant vs susceptible rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. PLoS ONE 7:e51609. 10.1371/journal.pone.0051609 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

