Protein Structure Classification and Loop Modeling Using Multiple Ramachandran Distributions
- PMID: 28280526
- PMCID: PMC5331158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2017.01.011
Protein Structure Classification and Loop Modeling Using Multiple Ramachandran Distributions
Abstract
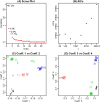
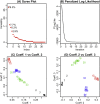
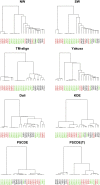
Recently, the study of protein structures using angular representations has attracted much attention among structural biologists. The main challenge is how to efficiently model the continuous conformational space of the protein structures based on the differences and similarities between different Ramachandran plots. Despite the presence of statistical methods for modeling angular data of proteins, there is still a substantial need for more sophisticated and faster statistical tools to model the large-scale circular datasets. To address this need, we have developed a nonparametric method for collective estimation of multiple bivariate density functions for a collection of populations of protein backbone angles. The proposed method takes into account the circular nature of the angular data using trigonometric spline which is more efficient compared to existing methods. This collective density estimation approach is widely applicable when there is a need to estimate multiple density functions from different populations with common features. Moreover, the coefficients of adaptive basis expansion for the fitted densities provide a low-dimensional representation that is useful for visualization, clustering, and classification of the densities. The proposed method provides a novel and unique perspective to two important and challenging problems in protein structure research: structure-based protein classification and angular-sampling-based protein loop structure prediction.
Keywords: Bivariate splines; Log-spline density estimation; Protein classification; Protein structure; Ramachandran distribution; Roughness penalty; SCOP; Trigonometric B-spline.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonparametric collective spectral density estimation with an application to clustering the brain signals.Stat Med. 2018 Dec 30;37(30):4789-4806. doi: 10.1002/sim.7972. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Stat Med. 2018. PMID: 30259540
-
New efficient statistical sequence-dependent structure prediction of short to medium-sized protein loops based on an exhaustive loop classification.J Mol Biol. 1999 Jun 25;289(5):1469-90. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2826. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10373380
-
Modeling angles in proteins and circular genomes using multivariate angular distributions based on multiple nonnegative trigonometric sums.Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2014 Feb;13(1):1-18. doi: 10.1515/sagmb-2012-0012. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24391194
-
Density Estimation for Protein Conformation Angles Using a Bivariate von Mises Distribution and Bayesian Nonparametrics.J Am Stat Assoc. 2009 Jun 1;104(486):586-596. doi: 10.1198/jasa.2009.0024. J Am Stat Assoc. 2009. PMID: 20221312 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing protein conformational sampling methods based on bivariate lag-distributions of backbone angles.Brief Bioinform. 2013 Nov;14(6):724-36. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs052. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Brief Bioinform. 2013. PMID: 22926831 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prediction of Protein Backbone Torsion Angles Using Deep Residual Inception Neural Networks.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019 May-Jun;16(3):1020-1028. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2814586. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29994074 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Inhibitory Potential of M. pendans Compounds Against N-Acetylglucosamine (Mur) Receptor: In Silico Insights Into Antibacterial Activity and Drug-Likeness.ScientificWorldJournal. 2024 Nov 30;2024:3569811. doi: 10.1155/tswj/3569811. eCollection 2024. ScientificWorldJournal. 2024. PMID: 39654692 Free PMC article.
-
In silico study reveals unconventional interactions between MDC1 of DDR and Beclin-1 of autophagy.Mol Divers. 2023 Dec;27(6):2789-2802. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10579-2. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 36482226
References
-
- Oldfield T.J., Hubbard R.E. Analysis of Cα geometry in protein structures. Proteins. 1994;18(4):324–337. - PubMed
-
- Laskowski R., MacArthur M.W., Moss D., Thornton J.M. Procheck: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr. 1993;26:283–291.
-
- Hooft R.W.W., Sander C., Vriend G. Objectively judging the quality of a protein structure from a Ramachandran plot. Comput Appl Biosci: CABIOS. 1997;13(4):425–430. - PubMed
-
- Simons K.T., Bonneau R., Ruczinski I., Baker D. Ab initio protein structure prediction of CASP III targets using ROSETTA. Proteins. 1999;37(Suppl 3):171–176. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
