Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm
- PMID: 28280714
- PMCID: PMC5322152
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00046
Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilm
Abstract
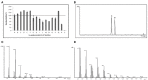
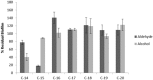
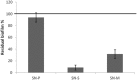
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a harmless human skin colonizer responsible for ~20% of orthopedic device-related infections due to its capability to form biofilm. Nowadays there is an interest in the development of anti-biofilm molecules. Marine bacteria represent a still underexploited source of biodiversity able to synthesize a broad range of bioactive compounds, including anti-biofilm molecules. Previous results have demonstrated that the culture supernatant of Antarctic marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125 impairs the formation of S. epidermidis biofilm. Further, evidence supports the hydrophobic nature of the active molecule, which has been suggested to act as a signal molecule. In this paper we describe an efficient activity-guided purification protocol which allowed us to purify this anti-biofilm molecule and structurally characterize it by NMR and mass spectrometry analyses. Our results demonstrate that the anti-biofilm molecule is pentadecanal, a long-chain fatty aldehyde, whose anti-S. epidermidis biofilm activity has been assessed using both static and dynamic biofilm assays. The specificity of its action on S. epidermidis biofilm has been demonstrated by testing chemical analogs of pentadecanal differing either in the length of the aliphatic chain or in their functional group properties. Further, indications of the mode of action of pentadecanal have been collected by studying the bioluminescence of a Vibrio harveyi reporter strain for the detection of autoinducer AI-2 like activities. The data collected suggest that pentadecanal acts as an AI-2 signal. Moreover, the aldehyde metabolic role and synthesis in the Antarctic source strain has been investigated. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the identification of an anti-biofilm molecule form from cold-adapted bacteria and on the action of a long-chain fatty aldehyde acting as an anti-biofilm molecule against S. epidermidis.
Keywords: Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC125; Staphylococcus epidermidis; anti-biofilm; long fatty acid aldehyde; quorum sensing.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

