Tracking daily fatigue fluctuations in multiple sclerosis: ecological momentary assessment provides unique insights
- PMID: 28281106
- PMCID: PMC5613039
- DOI: 10.1007/s10865-017-9840-4
Tracking daily fatigue fluctuations in multiple sclerosis: ecological momentary assessment provides unique insights
Abstract
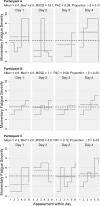
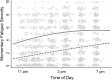
Studies investigating the prevalence, cause, and consequence of multiple sclerosis (MS) fatigue typically use single measures that implicitly assume symptom-stability over time, neglecting information about if, when, and why severity fluctuates. We aimed to examine the extent of moment-to-moment and day-to-day variability in fatigue in relapsing-remitting MS and healthy individuals, and identify daily life determinants of fluctuations. Over 4 weekdays, 76 participants (38 relapsing-remitting MS; 38 controls) recruited from multiple sites provided real-time self-reports six times daily (n = 1661 observations analyzed) measuring fatigue severity, stressors, mood, and physical exertion, and daily self-reports of sleep quality. Fatigue fluctuations were evident in both groups. Fatigue was highest in relapsing-remitting MS, typically peaking in late-afternoon. In controls, fatigue started lower and increased steadily until bedtime. Real-time stressors and negative mood were associated with increased fatigue, and positive mood with decreased fatigue in both groups. Increased fatigue was related to physical exertion in relapsing-remitting MS, and poorer sleep quality in controls. In relapsing-remitting MS, fatigue fluctuates substantially over time. Many daily life determinants of fluctuations are similar in relapsing-remitting MS and healthy individuals (stressors, mood) but physical exertion seems more relevant in relapsing-remitting MS and sleep quality most relevant in healthy individuals.
Keywords: Affect; Ambulatory assessment; Ecological momentary assessment; Fatigue; Multiple sclerosis; Psychological stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Daniel J. H. Powell, Christina Liossi, Wolff Schlotz, and Rona Moss-Morris declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights and Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Figures
References
-
- Barta WD, Tennen H, Litt MD. Measurement reactivity in diary research. In: Mehl MR, Conner TS, editors. Handbook of research methods for studying daily life. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2012.
-
- Black AC, Harel O, Matthews G. Techniques for analyzing intensive longitudinal data with missing values. In: Mehl MR, Conner TS, editors. Handbook of research methods for studying daily life. New York, NY: The Guilford Press; 2012.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

