Carnosine Attenuates the Development of both Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob Mice
- PMID: 28281693
- PMCID: PMC5345040
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44492
Carnosine Attenuates the Development of both Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob Mice
Abstract
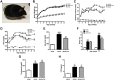
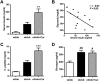
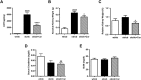
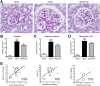
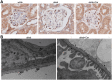
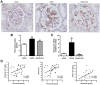
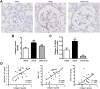
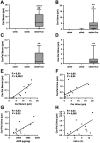
We previously demonstrated that polymorphisms in the carnosinase-1 gene (CNDP1) determine the risk of nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Carnosine, the substrate of the enzyme encoded by this gene, is considered renoprotective and could possibly be used to treat diabetic nephropathy (DN). In this study, we examined the effect of carnosine treatment in vivo in BTBR (Black and Tan, BRachyuric) ob/ob mice, a type 2 diabetes model which develops a phenotype that closely resembles advanced human DN. Treatment of BTBR ob/ob mice with 4 mM carnosine for 18 weeks reduced plasma glucose and HbA1c, concomitant with elevated insulin and C-peptide levels. Also, albuminuria and kidney weights were reduced in carnosine-treated mice, which showed less glomerular hypertrophy due to a decrease in the surface area of Bowman's capsule and space. Carnosine treatment restored the glomerular ultrastructure without affecting podocyte number, resulted in a modified molecular composition of the expanded mesangial matrix and led to the formation of carnosine-acrolein adducts. Our results demonstrate that treatment with carnosine improves glucose metabolism, albuminuria and pathology in BTBR ob/ob mice. Hence, carnosine could be a novel therapeutic strategy to treat patients with DN and/or be used to prevent DN in patients with diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gross J. L. et al.. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28, 164–176 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Bergrem H. & Leivestad T. Diabetic nephropathy and end-stage renal failure: the Norwegian story. Adv Ren Replace Ther 8, 4–12 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Gaede P., Lund-Andersen H., Parving H. H. & Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358, 580–591 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Krolewski M., Eggers P. W. & Warram J. H. Magnitude of end-stage renal disease in IDDM: a 35 year follow-up study. Kidney Int 50, 2041–2046 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Schena F. P. & Gesualdo L. Pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16, S30–33 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

