Differences in Right Ventricular Functional Changes during Treatment between Systemic Sclerosis-associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 28282243
- PMCID: PMC5802595
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201608-655OC
Differences in Right Ventricular Functional Changes during Treatment between Systemic Sclerosis-associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Patients with systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (SSc-PAH) continue to have an unacceptably high mortality rate despite the progress achieved with pulmonary arterial vasodilator therapies.
Objectives: We sought to determine whether SSc-PAH is a clinically distinct pulmonary vascular disease phenotype when compared with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) on the basis of progression of echocardiographic right ventricular (RV) dysfunction.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of echocardiographic data in 13 patients with SSc-PAH and 11 patients with IPAH was used to delineate the progression of RV dysfunction during single or combination pulmonary arterial vasodilator therapy. All patients had right heart catheterization-confirmed pulmonary arterial hypertension as well as complete baseline (at the time of diagnosis) and follow-up (most recent) echocardiograms. We excluded patients with significant scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease. Adjusting for time of follow-up and disease duration, we performed mixed model regression analyses comparing the changes between the two groups for different echocardiographic variables: tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, tricuspid regurgitation jet velocity, right atrial area, and RV diameter.
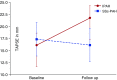
Results: The mean ages for the SSc-PAH and IPAH groups were 60.8 and 48.2 years, respectively. The mean follow-up periods for the two groups were 3.8 and 1.95 years, respectively. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion did not improve in patients with SSc-PAH, whereas it increased in the patients with IPAH (-0.38 mm, P = 0.87; vs. +5.6 mm, P = 0.02). The other echocardiographic variables showed a trend toward worsening in the SSc-PAH group and improvement in the IPAH group.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that, in patients with SSc-PAH, echocardiographic RV function does not improve over time compared with that of patients with IPAH, despite institution of pulmonary artery vasodilator therapies.
Keywords: disease progression; idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension; pulmonary arterial hypertension; right ventricle; systemic sclerosis–associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Figures

References
-
- Condliffe R, Kiely DG, Peacock AJ, Corris PA, Gibbs JS, Vrapi F, Das C, Elliot CA, Johnson M, DeSoyza J, et al. Connective tissue disease–associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern treatment era. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:151–157. - PubMed
-
- Lefèvre G, Dauchet L, Hachulla E, Montani D, Sobanski V, Lambert M, Hatron PY, Humbert M, Launay D. Survival and prognostic factors in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2412–2423. - PubMed
-
- Rubenfire M, Huffman MD, Krishnan S, Seibold JR, Schiopu E, McLaughlin VV. Survival in systemic sclerosis with pulmonary arterial hypertension has not improved in the modern era. Chest. 2013;144:1282–1290. - PubMed
-
- Muangchan C, Canadian Scleroderma Research Group, Markland J, Robinson D, Jones N, Khalidi N, Docherty P, Kaminska E, Masetto A, Sutton E, et al. The 15% rule in scleroderma: the frequency of severe organ complications in systemic sclerosis. A systematic review J Rheumatol 2013401545–1556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

