Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age
- PMID: 28282701
- PMCID: PMC6464706
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008524.pub3
Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age
Update in
-
Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from six months to five years of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 16;3(3):CD008524. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008524.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35294044 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) is a major public health problem in low- and middle-income countries, affecting 190 million children under five years of age and leading to many adverse health consequences, including death. Based on prior evidence and a previous version of this review, the World Health Organization has continued to recommend vitamin A supplementation for children aged 6 to 59 months. There are new data available from recently published randomised trials since the previous publication of this review in 2010, and this update incorporates this information and reviews the evidence.
Objectives: To assess the effects of vitamin A supplementation (VAS) for preventing morbidity and mortality in children aged six months to five years.
Search methods: In March 2016 we searched CENTRAL, Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, six other databases, and two trials registers. We also checked reference lists and contacted relevant organisations and researchers to identify additional studies.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and cluster-RCTs evaluating the effect of synthetic VAS in children aged six months to five years living in the community. We excluded studies involving children in hospital and children with disease or infection. We also excluded studies evaluating the effects of food fortification, consumption of vitamin A rich foods, or beta-carotene supplementation.
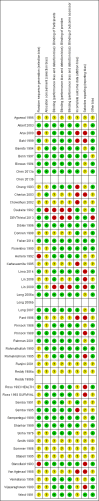
Data collection and analysis: For this update, two reviewers independently assessed studies for inclusion and abstracted data, resolving discrepancies by discussion. We performed meta-analyses for outcomes, including all-cause and cause-specific mortality, disease, vision, and side effects. We used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of the evidence.
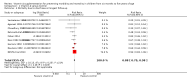
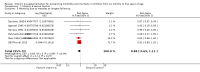
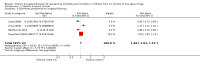
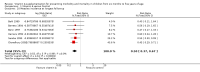
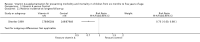
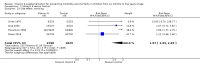
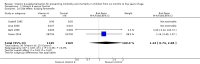
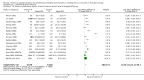
Main results: We identified 47 studies (4 of which are new to this review), involving approximately 1,223,856 children. Studies took place in 19 countries: 30 (63%) in Asia, 16 of these in India; 8 (17%) in Africa; 7 (15%) in Latin America, and 2 (4%) in Australia. About one-third of the studies were in urban/periurban settings, and half were in rural settings; the remaining studies did not clearly report settings. Most of the studies included equal numbers of girls and boys and lasted about a year. The included studies were at variable overall risk of bias; however, evidence for the primary outcome was at low risk of bias. A meta-analysis for all-cause mortality included 19 trials (1,202,382 children). At longest follow-up, there was a 12% observed reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality for vitamin A compared with control using a fixed-effect model (risk ratio (RR) 0.88, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.83 to 0.93; high-quality evidence). This result was sensitive to choice of model, and a random-effects meta-analysis showed a different summary estimate (24% reduction: RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.66 to 0.88); however, the confidence intervals overlapped with that of the fixed-effect model. Nine trials reported mortality due to diarrhoea and showed a 12% overall reduction for VAS (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.79 to 0.98; 1,098,538 participants; high-quality evidence). There was no significant effect for VAS on mortality due to measles, respiratory disease, and meningitis. VAS reduced incidence of diarrhoea (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.82 to 0.87; 15 studies; 77,946 participants; low-quality evidence) and measles (RR 0.50, 95% CI 0.37 to 0.67; 6 studies; 19,566 participants; moderate-quality evidence). However, there was no significant effect on incidence of respiratory disease or hospitalisations due to diarrhoea or pneumonia. There was an increased risk of vomiting within the first 48 hours of VAS (RR 1.97, 95% CI 1.44 to 2.69; 4 studies; 10,541 participants; moderate-quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: Vitamin A supplementation is associated with a clinically meaningful reduction in morbidity and mortality in children. Therefore, we suggest maintaining the policy of universal supplementation for children under five years of age in populations at risk of VAD. Further placebo-controlled trials of VAS in children between six months and five years of age would not change the conclusions of this review, although studies that compare different doses and delivery mechanisms are needed. In populations with documented vitamin A deficiency, it would be unethical to conduct placebo-controlled trials.
Conflict of interest statement
The World Health Organization (WHO) funded this review. The authors alone are responsible for the opinions and views expressed in this publication.
Aamer Imdad was paid for writing this review by the WHO. Evan Mayo‐Wilson ‐ none known. Zulfiqar A Bhutta's (ZB) institution received a grant from the WHO for this review and two additional vitamin A related Cochrane reviews (Imdad 2016; Haider 2017). ZB is an Editor for Cochrane Developmental, Pyschosocial and Learning Problems.
Figures




















Update of
-
Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in children from 6 months to 5 years of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Dec 8;(12):CD008524. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008524.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 11;3:CD008524. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008524.pub3. PMID: 21154399 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Agarwal 1995 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal DK, Pandey CM, Agarwal KN. Vitamin A administration and preschool child mortality. Nutrition Research 1995;15(5):669‐80. [DOI: 10.1016/0271-5317(95)00034-G] - DOI
Albert 2003 {published data only}
-
- Albert MJ, Qadri F, Wahed MA, Ahmed T, Rahman A, Ahmed F, et al. Supplementation with zinc, but not vitamin A, improves seroconversion to vibriocidal antibody in children given an oral cholera vaccine. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2003;187(6):909‐13. [PUBMED: 12660937] - PubMed
Arya 2000 {published data only}
-
- Arya S, Chellani H, Pandey J. Evaluation of safety of oral vitamin 'A' megadose co‐administered with measles vaccination. Indian Pediatrics 2000;37(12):1341‐7. [PUBMED: 11119336] - PubMed
Bahl 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bahl R, Kumar R, Bhandari N, Kant S, Srivastava R, Bhan MK. Vitamin A administered with measles vaccine to nine‐month‐old infants does not reduce vaccine immunogenicity. Journal of Nutrition 1999; Vol. 129, issue 8:1569‐73. [PUBMED: 10419992] - PubMed
Barreto 1994 {published data only}
-
- Andreozzi VL, Bailey TC, Nobre FF, Struchiner CJ, Barreto ML, Assis AM, et al. Random‐effects models in investigating the effect of vitamin A in childhood diarrhea. Annals of Epidemiology 2006;16(4):241‐7. [PUBMED: 16303315] - PubMed
-
- Barreto ML, Santos LM, Assis AM, Araújo MP, Farenzena GG, Santos PA, et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on diarrhoea and acute lower‐respiratory‐tract infections in young children in Brazil. Lancet 1994; Vol. 344, issue 8917:228‐31. [PUBMED: 7913157] - PubMed
Benn 1997 {published data only}
-
- Benn CS, Aaby P, Balé C, Olsen J, Michaelsen KF, George E, et al. Randomised trial of effect of vitamin A supplementation on antibody response to measles vaccine in Guinea‐Bissau, West Africa. Lancet 1997;350(9071):101‐5. [PUBMED: 9228962] - PubMed
-
- Benn CS, Lisse IM, Bale C, Michaelsen KF, Olsen J, Hedegaard K, et al. No strong long‐term effect of vitamin A supplementation in infancy on CD4 and CD8 T‐cell subsets. A community study from Guinea‐Bissau, West Africa. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2000;20(4):259‐64. [PUBMED: 11219162] - PubMed
Biswas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Biswas R, Biswas AB, Manna B, Bhattacharya SK, Dey R, Sarkar S. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on diarrhoea and acute respiratory tract infection in children. A double blind placebo controlled trial in a Calcutta slum community. European Journal of Epidemiology 1994;10(1):57‐61. [PUBMED: 7957792] - PubMed
Chen 2013a {published data only}
-
- Chen K, Chen XR, Zhang L, Luo HY, Gao N, Wang J, et al. Effect of simultaneous supplementation of vitamin A and iron on diarrheal and respiratory tract infection in preschool children in Chengdu City, China. Nutrition 2013;29(10):1197‐203. [PUBMED: 24012086] - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Zhang L, Luo H, Wang J, Li Q, Mao M. Effect of vitamin A supplements on iron metabolic homeostasis for preschoolers. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine 2014;48(1):18‐22. [PUBMED: 24713285] - PubMed
Chen 2013b {published data only}
-
- Chen K, Chen XR, Zhang L, Luo HY, Gao N, Wang J, et al. Effect of simultaneous supplementation of vitamin A and iron on diarrheal and respiratory tract infection in preschool children in Chengdu City, China. Nutrition 2013;29(10):1197‐203. [PUBMED: 24012086] - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Zhang L, Luo H, Wang J, Li Q, Mao M. Effect of vitamin A supplements on iron metabolic homeostasis for preschoolers. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine 2014;48(1):18‐22. [PUBMED: 24713285] - PubMed
Cheng 1993 {published data only}
-
- Lie C, Ying C, Wang EL, Brun T, Geissler C. Impact of large‐dose vitamin A supplementation on childhood diarrhoea, respiratory disease and growth. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1993;47(2):88‐96. [PUBMED: 8436094] - PubMed
Cherian 2003 {published data only}
Chowdhury 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chowdhury S, Kumar R, Ganguly NK, Kumar L, Walia BN. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on childhood morbidity and mortality. Indian Journal of Medical Sciences 2002;56(6):259‐64. [PUBMED: 12649946] - PubMed
Daulaire 1992 {published data only}
DEVTA trial 2013 {published data only}
-
- Awasthi S, Peto R, Bundy D, Read S, Kourellias K, Clark S, et al. Six‐monthly vitamin A supplementation from 1 to 6 years of age. Abstract of talk at ILSI Micronutrient Forum, 2007 April 16‐18, Istanbul.
Dibley 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dibley MJ, Sadjimin T, Kjolhede CL, Moulton LH. Vitamin A supplementation fails to reduce incidence of acute respiratory illness and diarrhea in preschool‐age Indonesian children. Journal of Nutrition 1996;126(2):434‐42. [PUBMED: 8632216] - PubMed
-
- Hadi H, Stoltzfus RJ, Dibley MJ, Moulton LH, West KP Jr, Kjolhede CL, et al. Vitamin A supplementation selectively improves the linear growth of Indonesian preschool children: results from a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2000;71(2):507‐13. [PUBMED: 10648265] - PubMed
-
- Hadi H, Stoltzfus RJ, Moulton LH, Dibley MJ, West KP Jr. Respiratory infections reduce the growth response to vitamin A supplementation in a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28(5):874‐81. [PUBMED: 10597985] - PubMed
Donnen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Donnen P, Brasseur D, Dramaix M, Vertongen F, Zihindula M, Muhamiriza M, et al. Vitamin A supplementation but not deworming improves growth of malnourished preschool children in eastern Zaire. Journal of Nutrition 1998;128(8):1320‐7. [PUBMED: 9687551] - PubMed
-
- Donnen P, Dramaix M, Brasseur D, Zihindula M, Muhamiriza M, Hennart P. Malnourished children morbidity following vitamin A supplementation or deworming in Democratic Republic of Congo. Archives of Public Health 1998;56:109‐24.
Fisker 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fisker AB, Bale C, Jørgensen MJ, Balde I, Hornshøj L, Bibby BM, et al. High‐dose vitamin A supplementation administered with vaccinations after 6 months of age: sex‐differential adverse reactions and morbidity. Vaccine 2013;31(31):3191‐8. [PUBMED: 23680441] - PubMed
-
- Fisker AB, Bale C, Rodrigues A, Balde I, Fernandes M, Jørgensen MJ, et al. High‐dose vitamin A with vaccination after 6 months of age: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2014;134(3):e739‐e48. [PUBMED: 25136048] - PubMed
-
- Fisker AB, Bale C, Rodrigues A, Jorgensen MJ, Danneskiold‐Sorensen N, Hornshoj L, et al. A randomised trial of high‐dose vitamin A at vaccination contacts after 6 months of age: sex‐differential effects on mortality. European Journal of Epidemiology 2013;28(1 Suppl 1):S229‐S30.
-
- Jensen KJ, Fisker AB, Andersen A, Sartono E, Yazdanbakhsh M, Aaby P, et al. The effects of vitamin A supplementation with measles vaccine on leucocyte counts and in vitro cytokine production. British Journal of Nutrition 2016;115(4):619‐28. [PUBMED: 26678511] - PubMed
Florentino 1990 {published data only}
-
- Florentino RF, Tanchoco CC, Ramos AC, Mendoza TS, Natividad EP, Tangco JB, et al. Tolerance of preschoolers to two dosage strengths of vitamin A preparation. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1990;52(4):694‐700. [PUBMED: 2403062] - PubMed
Herrera 1992 {published data only}
-
- Fawzi WW, Herrera MG, Willett WC, Amin A, Nestel P, Lipsitz S, et al. Vitamin A supplementation and dietary vitamin A in relation to the risk of xerophthalmia. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1993;58(3):385‐91. [PUBMED: 8237850] - PubMed
-
- Fawzi WW, Herrera MG, Willett WC, Nestel P, Amin A, Lipsitz S, et al. Dietary vitamin A intake and the risk of mortality among children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994;59(2):401‐8. [PUBMED: 8310992] - PubMed
-
- Fawzi WW, Herrera MG, Willett WC, Nestel P, Amin A, Mohamed KA. Dietary vitamin A intake and the incidence of diarrhea and respiratory infection among Sudanese children. Journal of Nutrition 1995;125(5):1211‐21. [PUBMED: 7738681] - PubMed
-
- Herrera MG, Nestel P, Amin A, Fawzi WW, Mohamed KA, Weld L. Vitamin A supplementation and child survival. Lancet 1992;340(8814):267‐71. [PUBMED: 1353192] - PubMed
Kartasasmita 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kartasasmita CB, Rosmayudi O, Deville W, Demedts M. Plasma retinol level, vitamin A supplementation and acute respiratory infections in children of 1‐5 years old in a developing country. Tubercle and Lung Disease 1995;76(6):563‐9. [PUBMED: 8593380] - PubMed
Lima 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lima AA, Soares AM, Lima NL, Mota RM, Maciel BL, Kvalsund MP, et al. Effects of vitamin A supplementation on intestinal barrier function, growth, total parasitic, and specific Giardia spp infections in Brazilian children: a prospective randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2010;50(3):309‐15. [DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181a96489; PMC2830290; PUBMED: 20038852] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lima AAM, Anstead GM, Zhang Q, Figueiredo IL, Soares AM, Mota RMS, et al. Effects of glutamine alone or in combination with zinc and vitamin A on growth, intestinal barrier function, stress and satiety‐related hormones in Brazilian shantytown children. Clinics 2014;69(4):225‐33. [DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2014(04)02] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lima AAM, Kvalsund MP, Souza PPE, Figueiredo IL, Soares AM, Mota RMS, et al. Zinc, vitamin A, and glutamine supplementation in Brazilian shantytown children at risk for diarrhea results in sex‐specific improvements in verbal learning. Clinics 2013;68(3):351‐8. [DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2013(03)OA11] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lin J, Song F, Yao P, Yang X, Li N, Sun S, et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on immune function of well‐nourished children suffering from vitamin A deficiency in China. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;62(12):1412‐8. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602881; PUBMED: 17684522] - DOI - PubMed
Lin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lin J, Lai X, Qin J, Song F, Zhang Y, Yao P, et al. Effect of beta‐carotene supplementation on health and growth of vitamin A deficient children in China rural villages: a randomized controlled trial. e‐SPEN, the European e‐Journal of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism 2009;4(1):e17‐e21. [DOI: 10.1016/j.eclnm.2008.09.001] - DOI
Long 2006a {published data only}
-
- Long K, Moran N, Santos J, Rosado J, Estrada‐Garcia T. Impact of vitamin A and zinc on diarrheal e. Coli infections and associated diarrheal episodes among children in Mexico City, Mexico. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. Abstracts of the 20th International Congress of Nutrition; 2013 September 15‐20; Granada, Spain. 2013; Vol. 63 (Suppl 1):170.
-
- Long K, Vasan P, Raga H, Santos J, Rosado J, Mamun A. Household water access and sanitation as indicators of vitamin A and zinc efficacy on gut parasite resolution. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. Abstracts of the 20th International Congress of Nutrition; 2013 September 15‐20; Granada, Spain. 2013; Vol. 63 (Suppl 1):221.
-
- Long KZ, Montoya Y, Hertzmark E, Santos JI, Rosado JL. A double‐blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;83(3):693‐700. [PUBMED: 16522919] - PubMed
-
- Rosado JL, Caamaño MC, Montoya YA, Lourdes Solano MdL, Santos JI, Long KZ. Interaction of zinc or vitamin A supplementation and specific parasite infections on Mexican infants' growth: a randomized clinical trial. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2009;63(10):1176‐84. [PUBMED: 19623197] - PubMed
Long 2006b {published data only}
-
- Long KZ, Montoya Y, Hertzmark E, Santos JI, Rosado JL. A double‐blind, randomized, clinical trial of the effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on diarrheal disease and respiratory tract infections in children in Mexico City, Mexico. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;83(3):693‐700. [PUBMED: 16522919] - PubMed
Long 2007 {published data only}
-
- Long KZ, Estrada‐Garcia T, Rosado JL, Santos JI, Haas M, Firestone M, et al. The effect of vitamin A supplementation on the intestinal immune response in Mexican children is modified by pathogen infections and diarrhea. Journal of Nutrition 2006;136(5):1365‐70. [PUBMED: 16614431] - PubMed
-
- Long KZ, Rosado JL, DuPont HL, Hertzmark E, Santos JI. Supplementation with vitamin A reduces watery diarrhoea and respiratory infections in Mexican children. British Journal of Nutrition 2007;97(2):337‐43. [PUBMED: 17298703] - PubMed
-
- Long KZ, Santos JI, Rosado JL, Lopez‐Saucedo C, Thompson‐Bonilla R, Abonce M, et al. Impact of vitamin A on selected gastrointestinal pathogen infections and associated diarrheal episodes among children in Mexico City, Mexico. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2006;194(9):1217‐25. [PUBMED: 17041847] - PubMed
Pant 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pokharel GP, Pant CR, Tilden RL, Pokhrel RP, Atmarita, Curtale F. Nutrition education and mega‐dose vitamin A supplementation in Nepal. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1998;65(4):547‐55. [PUBMED: 10773903] - PubMed
Pinnock 1986 {published data only}
-
- Pinnock CB, Douglas RM, Badcock NR. Vitamin A status in children who are prone to respiratory tract infections. Australian Paediatric Journal 1986;22(2):95‐9. [PUBMED: 3524531] - PubMed
Pinnock 1988 {published data only}
-
- Pinnock CB, Douglas RM, Martin AJ, Badcock NR. Vitamin A status of children with a history of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infancy. Australian Paediatric Journal 1988;24(5):286‐9. [PUBMED: 3067695] - PubMed
Rahman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rahman MM, Tofail F, Wahed MA, Fuchs GJ, Baqui AH, Alvarez JO. Short‐term supplementation with zinc and vitamin A has no significant effect on the growth of undernourished Bangladeshi children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;75(1):87‐91. [PUBMED: 11756064] - PubMed
-
- Rahman MM, Wahed MA, Fuchs GJ, Baqui AH, Alvarez JO. Synergistic effect of zinc and vitamin A on the biochemical indexes of vitamin A nutrition in children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;75(1):92‐8. [PUBMED: 11756065] - PubMed
Rahmathullah 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rahmathullah L. Effect of receiving a weekly dose of vitamin A equivalent to the recommended dietary allowances among pre school children on mortality in south India. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1991;58(6):837‐47. [PUBMED: 1818881] - PubMed
-
- Rahmathullah L, Underwood BA, Thulasiraj RD, Milton RC. Diarrhea, respiratory infections, and growth are not affected by a weekly low‐dose vitamin A supplement: a masked, controlled field trial in children in southern India. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991;54(3):568‐77. [PUBMED: 1877512] - PubMed
-
- Rahmathullah L, Underwood BA, Thulasiraj RD, Milton RC, Ramaswamy K, Rahmathullah R, et al. Reduced mortality among children in southern India receiving a small weekly dose of vitamin A. New England Journal of Medicine 1990;323(14):929‐35. [PUBMED: 2205798] - PubMed
-
- Rahmathullah L, Underwood BA, Thulasiraj RD, Milton RC, Ramaswamy K, Rahmathullah R, et al. Vitamin A supplementation reduces childhood mortality. National Medical Journal of India 1991;4(4):187‐9. - PubMed
Ramakrishnan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ramakrishnan U, Latham MC, Abel R. Vitamin A supplementation does not improve growth of preschool children: a randomized, double‐blind field trial in south India. Journal of Nutrition 1995;125(2):202‐11. [PUBMED: 7861247] - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishnan U, Latham MC, Abel R, Frongillo EA Jr. Vitamin A supplementation and morbidity among preschool children in south India. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;61(6):1295‐303. [PUBMED: 7762534] - PubMed
Ranjini 2001 {published data only}
-
- Cherian T, Ranjini EK, Balasubramaniam KA, Raghupathy P. Vitamin A supplementation in children with recurrent respiratory infections. Indian Pediatrics 2001;38(7):771‐5. [PUBMED: 11463965] - PubMed
Reddy 1986a {published data only}
-
- Reddy V, Vijayaraghavan K, Mathur KK. Effect of deworming and vitamin A administration on serum vitamin A levels in preschool children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1986;32(4):196‐9. [PUBMED: 3534284] - PubMed
Reddy 1986b {published data only}
-
- Reddy V, Vijayaraghavan K, Mathur KK. Effect of deworming and vitamin A administration on serum vitamin A levels in preschool children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1986;32(4):196‐9. [PUBMED: 3534284] - PubMed
Ross 1993 HEALTH {published data only}
-
- Benn CS, Aaby P, Nielsen J, Binka FN, Ross DA. Does vitamin A supplementation interact with routine vaccinations? An analysis of the Ghana Vitamin A Supplementation Trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2009;90(3):629‐39. [PUBMED: 19640958] - PubMed
-
- Binka FN, Ross DA, Morris SS, Kirkwood BR, Arthur P, Dollimore N, et al. Vitamin A supplementation and childhood malaria in northern Ghana. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;61(4):853‐9. [PUBMED: 7702031] - PubMed
-
- Dollimore N, Cutts F, Binka FN, Ross DA, Morris SS, Smith PG. Measles incidence, case fatality, and delayed mortality in children with or without vitamin A supplementation in rural Ghana. American Journal of Epidemiology 1997;146(8):646‐54. [PUBMED: 9345118] - PubMed
-
- Filteau SM, Morris SS, Raynes JG, Arthur P, Ross DA, Kirkwood BR, et al. Vitamin A supplementation, morbidity, and serum acute‐phase proteins in young Ghanaian children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;62(2):434‐8. [PUBMED: 7542831] - PubMed
-
- Filteau SM, Morris SS, Tomkins AM, Arthur P, Kirkwood BR, Ross DA, et al. Lack of association between vitamin A status and measures of conjunctival epithelial integrity in young children in northern Ghana. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994;48(9):669‐77. [PUBMED: 8001524] - PubMed
Ross 1993 SURVIVAL {published data only}
-
- Benn CS, Aaby P, Nielsen J, Binka FN, Ross DA. Does vitamin A supplementation interact with routine vaccinations? An analysis of the Ghana Vitamin A Supplementation Trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2009;90(3):629‐39. [PUBMED: 19640958] - PubMed
-
- Binka FN, Ross DA, Morris SS, Kirkwood BR, Arthur P, Dollimore N, et al. Vitamin A supplementation and childhood malaria in northern Ghana. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;61(4):853‐9. [PUBMED: 7702031] - PubMed
-
- Dollimore N, Cutts F, Binka FN, Ross DA, Morris SS, Smith PG. Measles incidence, case fatality, and delayed mortality in children with or without vitamin A supplementation in rural Ghana. American Journal of Epidemiology 1997;146(8):646‐54. [PUBMED: 9345118] - PubMed
-
- Filteau SM, Morris SS, Raynes JG, Arthur P, Ross DA, Kirkwood BR, et al. Vitamin A supplementation, morbidity, and serum acute‐phase proteins in young Ghanaian children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;62(2):434‐8. [PUBMED: 7542831] - PubMed
-
- Filteau SM, Morris SS, Tomkins AM, Arthur P, Kirkwood BR, Ross DA, et al. Lack of association between vitamin A status and measures of conjunctival epithelial integrity in young children in northern Ghana. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994;48(9):669‐77. [PUBMED: 8001524] - PubMed
Semba 1991 {published data only}
-
- Semba R, Muhilal, Scott A, Natadisastra G, Wirasasmita S, Griffin D, et al. Immune status in children with mild vitamin A deficiency in Indonesia. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Annual Meeting; 1991 April 28 ‐ May 3; Sarasota, FL. 1991; Vol. 32 (4).
-
- Semba RD, Muhilal MPH, West KP Jr, Winget M, Natadisastra G, Scott A, et al. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on hematological indicators of iron metabolism and protein status in children. Nutrition Research 1992;12(4‐5):469‐78. [DOI: 10.1016/S0271-5317(05)80017-X] - DOI
-
- Semba RD, Muhilal, Scott AL, Natadisastra G, Wirasasmita S, Mele L, et al. Depressed immune response to tetanus in children with vitamin A deficiency. Journal of Nutrition 1992;122(1):101‐7. [PUBMED: 1729457] - PubMed
Semba 1995 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD, Munasir Z, Beeler J, Akib A, Muhilal, Audet S, et al. Reduced seroconversion to measles in infants given vitamin A with measles vaccination. Lancet 1995;345(8961):1330‐2. [PUBMED: 7752754] - PubMed
Sempertegui 1999 {published data only}
-
- Sempértegui F, Estrella B, Camaniero V, Betancourt V, Izurieta R, Ortiz W, et al. The beneficial effects of weekly low‐dose vitamin A supplementation on acute lower respiratory infections and diarrhea in Ecuadorian children. Pediatrics 1999;104(1):e1. [PUBMED: 10390287] - PubMed
Shankar 1999 {published data only}
Sinha 1976 {published data only}
-
- Sinha DP, Bang FB. The effect of massive doses of vitamin A on the signs of vitamin A deficiency in preschool children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1976;29(1):110‐5. [PUBMED: 1082238] - PubMed
Smith 1999 {published data only}
-
- Smith JC, Makdani D, Hegar A, Rao D, Douglass LW. Vitamin A and zinc supplementation of preschool children. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1999;18(3):213‐22. [PUBMED: 10376776] - PubMed
Sommer 1986 {published data only}
-
- Djunaedi E, Sommer A, Pandji A, Kusdiono, Taylor HR. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on xerophthalmia. A randomized controlled community trial. Archives of Ophthalmology 1988;106(2):218‐22. [PUBMED: 3277608] - PubMed
-
- Sommer A, Tarwotjo I, Djunaedi E, West KP Jr, Loeden AA, Tilden R, et al. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on childhood mortality. A randomised controlled community trial. Lancet 1986;1(8491):1169‐73. [PUBMED: 2871418] - PubMed
-
- Tielsch JM, West KP Jr. Cost and efficiency considerations in community‐based trials of vitamin A in developing countries. Statistics in Medicine 1990; Vol. 9, issue 1‐2:35‐41; discussion 41‐3. [PUBMED: 2345837] - PubMed
Stabell 1995 {published data only}
-
- Stabell C, Balé C, Pedro da Silva A, Olsen J, Aaby P. No evidence of fontanelle‐bulging episodes after vitamin A supplementation of 6‐ and 9‐month‐old infants in Guinea Bissau. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;49(1):73‐4. [PUBMED: 7713054] - PubMed
Stansfield 1993 {published data only}
Van Agtmaal 1988 {published data only}
-
- Agtmaal EJ, Bloem MW, Speek AJ, Saowakontha S, Schreurs HP, Haeringen NJ. The effect of vitamin A supplementation on tear fluid retinol levels of marginally nourished preschool children. Current Eye Research 1988;7(1):43‐8. [PUBMED: 3359804] - PubMed
Venkatarao 1996 {published data only}
-
- Venkatarao T, Ramakrishnan R, Nair NG, Radhakrishnan S, Sundaramoorthy L, Koya PK, et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation to mother and infant on morbidity in infancy. Indian Pediatrics 1996; Vol. 33, issue 4:279‐86. [PUBMED: 8772901] - PubMed
Vijayaraghavan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Vijayaraghavan K, Radhaiah G, Surya Prakasam BS, Sarma KVR, Reddy V. Effect of massive dose vitamin A on morbidity and mortality in Indian children. Lancet 1990;336(8727):1342‐5. [PUBMED: 1978164] - PubMed
West 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bishai D, Kumar KCS, Waters H, Koenig M, Katz J, Khatry SK, et al. The impact of vitamin A supplementation on mortality inequalities among children in Nepal. Health Policy and Planning 2005;20(1):60‐6. [PUBMED: 15689431] - PubMed
-
- Katz J, West KP Jr, Khatry SK, Thapa MD, LeClerq SC, Pradhan EK, et al. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on prevalence and incidence of xerophthalmia in Nepal. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1995;36(13):2577‐83. [PUBMED: 7499080] - PubMed
-
- Shih JH, Lu SE. Analysis of failure time data with multilevel clustering, with application to the child vitamin a intervention trial in Nepal. Biometrics 2007; Vol. 63, issue 3:673‐80. [PUBMED: 17825001] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al‐Mekhlafi 2014 {published data only}
Bahl 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bahl R, Bhandari N, Taneja S, Bhan MK. The impact of vitamin A supplementation on physical growth of children is dependent on season. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1997; Vol. 51, issue 1:26‐9. [PUBMED: 9023463] - PubMed
Bhaskaram 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bhaskaram P, Rao KV. Enhancement in seroconversion to measles vaccine with simultaneous administration of vitamin A in 9‐months‐old Indian infants. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1997;64(4):503‐9. [PUBMED: 10771879] - PubMed
Bloem 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bloem MW, Wedel M, Agtmaal EJ, Speek AJ, Saowakontha S, Schreurs WHP. Vitamin A intervention: short‐term effects of a single, oral, massive dose on iron metabolism. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1990;51(1):76‐9. [PUBMED: 2296931] - PubMed
Chen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chen K, Li TY, Chen L, Qu P, Liu YX. Effects of vitamin A, vitamin A plus iron and multiple micronutrient‐fortified seasoning powder on preschool children in a suburb of Chongqing, China. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology 2008;54(6):440‐7. [PUBMED: 19155581] - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Liu YF, Chen L, Zhang X, Liu YX, Chen J, et al. Effects of vitamin A, vitamin A plus iron and multiple micronutrient‐fortified seasoning powder on iron metabolic homeostasis. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics 2011;49(12):926‐32. [PUBMED: 22336361] - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Liu YF, Gong M, Jiang W, Fan Z, Qu P, et al. Effects of vitamin A, vitamin A plus zinc, and multiple micronutrients on anemia in preschool children in Chongqing, China. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2012;21(1):3‐11. [PUBMED: 22374555] - PubMed
Chhagan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chhagan MK, Broeck J, Luabeya KK, Mpontshane N, Tomkins A, Bennish ML. Effect on longitudinal growth and anemia of zinc or multiple micronutrients added to vitamin A: a randomized controlled trial in children aged 6‐24 months. BMC Public Health 2010;10:145. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-145] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Edmond 2012 {published data only}
-
- Edmond KL, Hurt L, Fenty J, Amenga‐Etego S, Zandoh C, Hurt C, et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation in women of reproductive age on cause‐specific early and late infant mortality in rural Ghana: ObaapaVitA double‐blind, cluster‐randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. BMJ Open 2012;2(1):1‐10. [DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000658] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Fahmida 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fahmida U, Rumawas JSP, Utomo B, Patmonodewo S, Schultink W. Zinc‐iron, but not zinc‐alone supplementation, increased linear growth of stunted infants with low haemoglobin. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;16(2):301‐9. [PUBMED: 17468087] - PubMed
Ganon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gannon B, Kaliwile C, Arscott SA, Schmaelzle S, Chileshe J, Kalungwana N, et al. Biofortified orange maize is as efficacious as a vitamin A supplement in Zambian children even in the presence of high liver reserves of vitamin A: a community‐based, randomized placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014;100(6):1541‐50. [PUBMED: 25411289] - PMC - PubMed
Kartasurya 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kartasurya MI, Ahmed F, Subagio HW, Rahfiludin MZ, Marks GC. Zinc combined with vitamin A reduces upper respiratory tract infection morbidity in a randomised trial in preschool children in Indonesia. British Journal of Nutrition 2012;108(12):2251‐60. [PUBMED: 22414819] - PubMed
Kothari 1991 {published data only}
-
- Kothari G. The effect of vitamin A prophylaxis on morbidity and mortality among children in urban slums in Bombay. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1991;37(3):141. [PUBMED: 1861286] - PubMed
Nankabirwa 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nankabirwa V, Tylleskar T, Nankunda J, Engebretsen I, Sommerfelt H, Tumwine J. Poster presentation: prevalence of malaria parasitaemia among infants in Uganda and its association with breastfeeding, peer counselling and vitamin a supplementation. Tropical Medicine & International Health. Abstracts of the 7th European Congress on Tropical Medicine and International Health; 2011 October 3‐6; Barcelona, Spain. 2011; Vol. 16 Suppl s1:97.
-
- Nankabirwa V, Tylleskar T, Nankunda J, Engebretsen IM, Sommerfelt H, Tumwine JK. Malaria parasitaemia among infants and its association with breastfeeding peer counselling and vitamin A supplementation: a secondary analysis of a cluster randomized trial. PLOS ONE 2011;6(7):e21862. [PUBMED: 21760916] - PMC - PubMed
Owusu‐Agyei 2013 {published data only}
Semba 1990 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD, Wirasasmita S, Natadisastra G, Muhilal, Sommer A. Response of Bitot's spots in preschool children to vitamin A treatment. American Journal of Ophthalmology 1990;110(4):416‐20. [PUBMED: 2220978] - PubMed
Semba 2005 {published data only}
-
- Semba RD, Ndugwa C, Perry RT, Clark TD, Jackson JB, Melikian G, et al. Effect of periodic vitamin A supplementation on mortality and morbidity of human immunodeficiency virus‐infected children in Uganda: a controlled clinical trial. Nutrition 2005;21(1):25‐31. [PUBMED: 15661475] - PubMed
Wu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wu Z, Lin L, Ouyang L. Impact of vitamin A on the immune function of infants. China Tropical Medicine 2007;7(4):540‐1.
Yakymenko 2011 {published data only}
Yang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Yang YX, Han JH, Shao XP, He M, Bian LH, Wang Z, et al. Effect of micronutrient supplementation on the growth of preschool children in China. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences 2002;15(3):196‐202. [PUBMED: 12500659] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Aklamati 2006 {published data only}
-
- Aklamati E, Brown KH, Mulenga M, Kafwembe E, Peerson JM, Stephensen C, et al. Impact of high‐dose vitamin A supplements on vitamin A status of 3‐4 year old Zambian boys. FASEB Journal 2006;20(5):A1050.
Additional references
Alvarez 1995
-
- Alvarez JO, Salazar‐Lindo E, Kohatsu J, Miranda P, Stephensen CB. Urinary excretion of retinol in children with acute diarrhoea. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;61(6):1273‐6. [PUBMED: 7762530] - PubMed
Bates 1995
-
- Bates CJ. Vitamin A. Lancet 1995;345(8941):31‐5. [PUBMED: 7799706] - PubMed
Beaton 1993
-
- Beaton GH, Martorell R, Aronson KJ, Edmonston B, McCabe G, Ross AC, et al. Effectiveness of Vitamin A supplementation in the control of young child morbidity and mortality in developing countries ‐ nutrition policy discussion paper no. 13. www.unscn.org/layout/modules/resources/files/Policy_paper_No_13.pdf (accessed 23 March 2016).
Bello 2009
-
- Bello S, Meremikwu MM, Ejemot RI. Routine vitamin A supplementation for the prevention of blindness due to measles infection in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007719] - DOI
Bhutta 2015
Chen 2008
Darlow 2011
Fawzi 1993
Fawzi 2006
Glasziou 1993
Gogia 2011
Green 1928
Guyatt 2011
Habicht 2013
Haider 2017
Haskell 1999
-
- Haskell MJ, Brown KH. Maternal vitamin A nutriture and the vitamin A content of human milk. Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia 1999;4(3):243‐57. [PUBMED: 10527467] - PubMed
Hathcock 1997
-
- Hathcock JN. Vitamins and minerals: efficacy and safety. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1997;66(2):427‐37. [PUBMED: 9250127] - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Imdad 2010b
-
- Imdad A, Yakoob MY, Haider BA, Bhutta ZA. Preventive and therapeutic effects of vitamin A supplementation on infant and childhood morbidity and mortality: a systematic review. In: Bhutta ZA editor(s). Nutrition Interventions for Maternal and Child Health and Survival. Vol. 1, Oxford University Press, 2010:125‐39.
Imdad 2016
Irlam 2010
Katz 1995
-
- Katz J, West KP Jr, Khatry SK, Thapa MD, LeClerq SC, Pradhan EK, et al. Impact of vitamin A supplementation on prevalence and incidence of xerophthalmia in Nepal. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1995;36(13):2577‐83. [PUBMED: 7499080] - PubMed
Klemm 2009
-
- Klemm RD, West KJ, Tielsh J, Wu L, Katz J. TU54 poster presentation: pooled analysis of Asian newborn vitamin A supplementation trials to assess differential effects of early infant mortality. Micronutrients, Health and Development: Evidence‐based Programs. Proceedings of the 2nd International Meeting of the Micronutrient Forum; 2009 May 12‐15; Beijing, China. 2009.
Klemm 2010
-
- Klemm RD, West KP Jr, Palmer AC, Johnson Q, Randall P, Ranum P, et al. Vitamin A fortification of wheat flour: considerations and current recommendations. Food and Nutrition Bulletin 2010;31(1 Suppl):S47‐61. [PUBMED: 20629352] - PubMed
Klemm 2016
Mannar 2013
-
- Mannar V, Schultink W, Spahn K. Vitamin A supplementation in Indian children. Lancet 2013;382(9892):591‐2. [PUBMED: 23961552] - PubMed
Mayo‐Wilson 2007
Mayo‐Wilson 2011
Mayo‐Wilson 2013
Mitra 1998
-
- Mitra AK, Alvarez JO, Guay‐Woodford L, Fuchs GJ, Wahed MA, Stephenson CB. Urinary retinol excretion and kidney function in children with shigellosis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998;68(5):1095‐103. [PUBMED: 9808228] - PubMed
Moher 2009
Ni 2005
Peto 2013
Ramakrishnan 2002
-
- Ramakrishnan U, Darnton‐Hill I. Assessment and control of vitamin A deficiency disorders. Journal of Nutrition 2002;132(9 Suppl):2947‐53S. [PUBMED: 12221275] - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rice 2004
-
- Rice AL, West KP Jr, Black RE. Vitamin A Deficiency. Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors. Vol. 1, Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004.
Semba 1999
-
- Semba RD. Vitamin A and immunity to viral, bacterial and protozoan infections. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 1999;58(3):719‐27. [PUBMED: 10604208] - PubMed
Shenai 1993
-
- Shenai JP. Vitamin A. In: Tsang RC, Lucas A, Uauy R editor(s). Nutritional Needs of the Preterm Infant: Scientific Basis and Practical Guidelines. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1993:87‐100.
Sloan 2013
Smith 1976
-
- Smith FR, Goodman DS. Vitamin A transport in human vitamin A toxicity. New England Journal of Medicine 1976;294(15):805‐8. [PUBMED: 943041] - PubMed
Sommer 1996
-
- Sommer A, West KP Jr. Vitamin A Deficiency: Health, Survival and Vision. New York: Oxford University Press, 1996.
Sommer 2002
-
- Sommer A, Davidson FR, Annecy Accords. Assessment and control of vitamin A deficiency: the Annecy Accords. Journal of Nutrition 2002;132(9 Suppl):2845S‐50S. [PUBMED: 12221259] - PubMed
Sommer 2013
Stevens 2015
-
- Stevens GA, Bennett JE, Hennocq Q, Lu Y, De‐Regil LM, Rogers L, et al. Trends and mortality effects of vitamin A deficiency in children in 138 low‐income and middle‐income countries between 1991 and 2013: a pooled analysis of population‐based surveys. Lancet Global Health 2015;3(9):e528–36. [DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00039-X] - DOI - PubMed
US Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board
-
- US Institute of Medicine, Food, Nutrition Board. Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Washington (DC): National Academy Press, 2000.
Van den Broek 2002
Van Lieshout 2005
-
- Lieshout M, Pee S. Vitamin A equivalency estimates: understanding apparent differences. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;81(4):943‐5; author reply 945‐6. - PubMed
Villamor 2000
West 2002
-
- West CE, Eilander A, Lieshout M. Consequences of revised estimates of carotenoid bioefficacy for dietary control of vitamin A deficiency in developing countries. Journal of Nutrition 2002;132(9 Suppl):2920‐6S. [PUBMED: 12221270] - PubMed
West 2003
-
- West KP Jr. Vitamin A deficiency disorders in children and women. Food and Nutrition Bulletin 2003;4(4 Suppl):S78‐S90. [PUBMED: 17016949] - PubMed
WHO 2009
-
- World Health Organization. Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995–2005: WHO global database on vitamin A deficiency. apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44110/1/9789241598019_eng.pdf (accessed 23 March 2016).
Wiysonge 2011
References to other published versions of this review
Imdad 2010a
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

