Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Adiponectin in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 28282917
- PMCID: PMC5372608
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18030592
Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Adiponectin in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
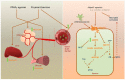
The adipocyte-secreted protein adiponectin (APN) has several protective functions in the peripheral tissues including insulin sensitizing, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects that may benefit neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition, dysregulation of cerebral insulin sensitivities and signaling activities have been implicated in AD. Emerging insights into the mechanistic roles of adiponectin and AD highlight the potential therapeutic effects for AD through insulin signaling.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β; adiponectin; cognitive impairments.
Conflict of interest statement
Koon-Ho Chan has received research funding support from Merck Pharmaceutical Ltd., Novartis Pharmaceutical Ltd., Bayer HealthCare Ltd., honorarium for invited lectures from Biogen Idec and UCH Pharma Ltd., and sponsorship to attend conferences from Novartis Pharmaceutical Ltd., Bayer HealthCare Ltd., UCH Pharma Ltd. and Sanofi Genzyme. Roy Chun-Laam Ng declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stelzmann R.A., Norman Schnitzlein H., Reed Murtagh F. Uber eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg. Z. Psychiatr. 1907;64:146–148. - PubMed
-
- Oakley H., Cole S.L., Logan S., Maus E., Shao P., Craft J., Guillozet-Bongaarts A., Ohno M., Disterhoft J., VanEldik L., et al. Intraneuronal β-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006;26:10129–10140. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-06.2006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

