Interferon regulatory factor signaling in autoimmune disease
- PMID: 28283223
- PMCID: PMC8033540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.02.006
Interferon regulatory factor signaling in autoimmune disease
Abstract
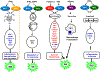
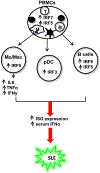
Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) play critical roles in pathogen-induced innate immune responses and the subsequent induction of adaptive immune response. Dysregulation of IRF signaling is therefore thought to contribute to autoimmune disease pathogenesis. Indeed, numerous murine in vivo studies have documented protection from or enhanced susceptibility to particular autoimmune diseases in Irf-deficient mice. What has been lacking, however, is replication of these in vivo observations in primary immune cells from patients with autoimmune disease. These types of studies are essential as the majority of in vivo data support a protective role for IRFs in Irf-deficient mice, yet IRFs are often found to be overexpressed in patient immune cells. A significant body of work is beginning to emerge from both of these areas of study - mouse and human.
Keywords: Autoimmune disease; Cell signaling; Interferon regulatory factors; Pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ning S, Interferon Regulatory Factors and Autoimmune Diseases. HSOA Journal of Medical Genomics and Biomarkers, 2014. 1.
-
- Honda K, Takaoka A, and Taniguchi T, Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity, 2006. 25(3): p. 349–60. - PubMed
-
- Tamura T, et al., The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol, 2008. 26: p. 535–84. - PubMed
-
- Battistini A, Interferon regulatory factors in hematopoietic cell differentiation and immune regulation. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2009. 29(12): p. 765–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

