Phase 1b study of pembrolizumab (MK-3475; anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) in Japanese patients with advanced melanoma (KEYNOTE-041)
- PMID: 28283736
- PMCID: PMC5364262
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-016-3237-x
Phase 1b study of pembrolizumab (MK-3475; anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) in Japanese patients with advanced melanoma (KEYNOTE-041)
Abstract
Purpose: This phase I b study evaluated the safety and anti-tumor activity of pembrolizumab in Japanese patients with advanced melanoma.
Methods: Pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg) was given every 3 weeks (Q3W) for up to 2 years or until confirmed progression or unacceptable toxicity. The tumor response was assessed as per the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 (RECIST v1.1) by both investigator review and central review.
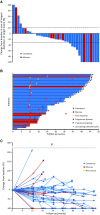
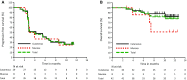
Results: Forty-two patients with advanced melanoma received pembrolizumab. A primary cutaneous histology was observed in 34 patients (81.0%), while a primary mucosal histology was observed in 8 patients (19.0%). Thirty-four patients (81.0%) experienced treatment-related adverse events (AEs). The most common treatment-related AEs were pruritus, maculopapular rash, malaise, and hypothyroidism. Grade 3-5 treatment-related AEs occurred in 8 patients (19.0%). The only grade 3-5 treatment-related AE reported in at least two patients was anemia. There were two treatment-related deaths (unknown cause and cerebral hemorrhage). Among the 37 evaluable patients, the confirmed overall response rates (ORRs) determined by central review were 24.1% (95% CI 10.3-43.5) for cutaneous melanoma and 25.0% (95% CI 3.2-65.1) for mucosal melanoma. The responses were durable, and the median duration of response was not reached in either population. The median overall survival (OS) was not reached, with a 12-month OS of 82.7% for cutaneous melanoma and 51.4% for mucosal melanoma.
Conclusion: The safety profile of pembrolizumab in Japanese patients was similar to that reported in the previous clinical studies. Pembrolizumab provided promising anti-tumor activity in Japanese patients with advanced melanoma.
Keywords: Anti-PD-1 therapy; Immunotherapy; Japanese patients; Melanoma; Pembrolizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This study was funded by MSD K.K. (Tokyo, Japan).
Conflict of interest
K. Nakagawa received a speaker honoraria from Astellas, AstraZeneca, EPS Holdings, Ono Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Showa Yakuhin Kako, SymBio Pharmaceuticals, Daiichi Sankyo, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly Japan, Pfizer Japan, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and received research grants funding from Chugai Pharmaceutical, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, EPS Associates, Quintiles, Daiichi Sankyo, Japan Clinical Research Operations, Eisai, PPD-SNBL, Pfizer Japan, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. H. Uhara received a speaker honorarium from MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Novartis Pharma, Roche Diagnostics, and Mochida Pharmaceutical, and received research grants from Ono Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, and Mochida Pharmaceutical. T. Takenouchi received a speaker honorarium from MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical, and Novartis Pharma. Y. Kiyohara received research grants from Ono Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Merck Serono, GlaxoSmithKline, and received a speaker honorarium from Ono Pharmaceutical, and Chugai Pharmaceutical, and reported the safety review committee role of Ono Pharmaceutical, and Chugai Pharmaceutical. T. Shimamoto and K. Noguchi are employees of MSD K.K. and hold stock in Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. N. Yamazaki, M. Fujimoto, H. Ihn, H. Uchi, T. Inozume, H. Furukawa, H. Wada, and K. Yokota declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards established in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. The study was approved by the institutional review board of each study site, and all the patients provided informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

