Combination of glycopyrronium and indacaterol inhibits carbachol-induced ERK5 signal in fibrotic processes
- PMID: 28284212
- PMCID: PMC5346259
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-017-0529-6
Combination of glycopyrronium and indacaterol inhibits carbachol-induced ERK5 signal in fibrotic processes
Abstract
Background: Airway fibrosis is one of the pathological features of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and recent studies revealed that acetylcholine plays an important role in the development of airway remodeling by stimulating proliferation and collagen synthesis of lung fibroblasts. This study was designed to examine the effects of a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrronium and a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) indacaterol on acetylcholine-mediated fibrotic responses in lung fibroblasts.
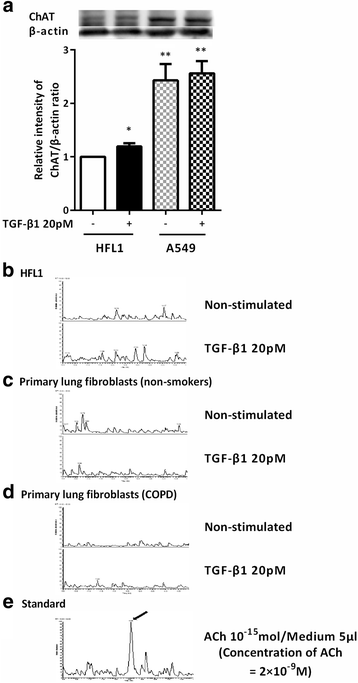
Methods: After carbachol (CCh) or transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) exposure, the response to glycopyrronium and indacaterol was determined in vitro in fibroblasts isolated from mild-to-moderate COPD lung tissue. The ability of fibroblasts to mediate the contraction of collagen gels was assessed. The expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) were determined by immunoblot. TGF-β1 was quantified by ELISA and acetylcholine was quantified by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry.
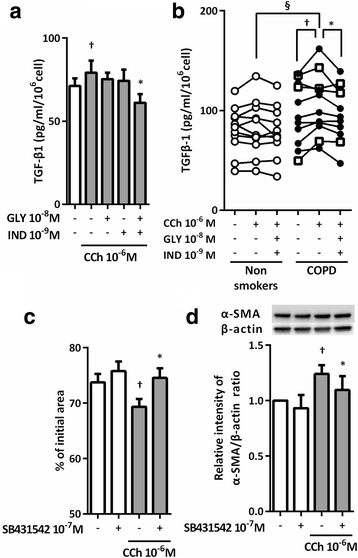
Results: CCh stimulated fibroblast-mediated collagen gel contraction and α-SMA expression and TGF-β1 release by fibroblasts. Blockade of autocrine TGF-β1 attenuated CCh-mediated fibrotic responses, while TGF-β1 did not stimulate acetylcholine release. Glycopyrronium plus indacaterol significantly attenuated CCh- and TGF-β1-mediated fibrotic responses through inhibition of ERK5 phosphorylation. Notably, the magnitudes of CCh- and TGF-β1-stimulated gel contraction, CCh-induced TGF-β1 release, and ERK5 phosphorylation were greater in fibroblasts isolated from COPD subjects than in those from non-smokers.
Conclusions: CCh induced TGF-β1 self-sustaining signaling loops by potentiating ERK5 signaling and promoted myofibroblast activity. This autocrine signaling mechanism may be an attractive therapeutic target to block the fibrotic response, which was modulated by the combination of glycopyrronium and indacaterol.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5); Long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist; Long-acting β2-adrenergic receptor agonist; Transforming growth factor-β1.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Specific Features of Fibrotic Lung Fibroblasts Highly Sensitive to Fibrotic Processes Mediated via TGF-β-ERK5 Interaction.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):822-837. doi: 10.33594/000000057. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30946557
-
Combination of roflumilast with a beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist inhibits proinflammatory and profibrotic mediator release from human lung fibroblasts.Respir Res. 2012 Mar 27;13(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-28. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 22452977 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography (CT)-assessed bronchodilation induced by inhaled indacaterol and glycopyrronium/indacaterol in COPD.Respir Med. 2016 Oct;119:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.08.020. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27692151 Clinical Trial.
-
Combination therapy with indacaterol and glycopyrronium bromide in the management of COPD: an update on the evidence for efficacy and safety.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015 Apr;9(2):49-55. doi: 10.1177/1753465815572065. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015. PMID: 25691493 Review.
-
Profile of inhaled glycopyrronium bromide as monotherapy and in fixed-dose combination with indacaterol maleate for the treatment of COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015 Jan 7;10:111-23. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S67758. eCollection 2015. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015. PMID: 25609944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Acetylcholine and Muscarinic Receptors in Allergic Rhinitis: Mechanisms, Clinical Insights and Future Directions.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025 Sep 11;25(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s11882-025-01221-w. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2025. PMID: 40932538 Review.
-
Sublytic C5b-9 induces proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells via ERK5/MZF1/RGC-32 axis activated by FBXO28-TRAF6 complex.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Aug;23(8):5654-5671. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14473. Epub 2019 Jun 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31184423 Free PMC article.
-
Pirfenidone attenuates lung fibrotic fibroblast responses to transforming growth factor-β1.Respir Res. 2019 Jun 11;20(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1093-z. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31185973 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast-specific ERK5 deficiency changes tumor vasculature and exacerbates tumor progression in a mouse model.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;393(7):1239-1250. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01859-5. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32307577
References
-
- Takizawa H, Tanaka M, Takami K, Ohtoshi T, Ito K, Satoh M, Okada Y, Yamasawa F, Nakahara K, Umeda A. Increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in small airway epithelium from tobacco smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1476–1483. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.6.9908135. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

