Use of Nintendo Wii Balance Board for posturographic analysis of Multiple Sclerosis patients with minimal balance impairment
- PMID: 28284217
- PMCID: PMC5346266
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-017-0230-5
Use of Nintendo Wii Balance Board for posturographic analysis of Multiple Sclerosis patients with minimal balance impairment
Abstract
Background: The Wii Balance Board (WBB) has been proposed as an inexpensive alternative to laboratory-grade Force Plates (FP) for the instrumented assessment of balance. Previous studies have reported a good validity and reliability of the WBB for estimating the path length of the Center of Pressure. Here we extend this analysis to 18 balance related features extracted from healthy subjects (HS) and individuals affected by Multiple Sclerosis (MS) with minimal balance impairment.
Methods: Eighteen MS patients with minimal balance impairment (Berg Balance Scale 53.3 ± 3.1) and 18 age-matched HS were recruited in this study. All subjects underwent instrumented balance tests on the FP and WBB consisting of quiet standing with the eyes open and closed. Linear correlation analysis and Bland-Altman plots were used to assess relations between path lengths estimated using the WBB and the FP. 18 features were extracted from the instrumented balance tests. Statistical analysis was used to assess significant differences between the features estimated using the WBB and the FP and between HS and MS. The Spearman correlation coefficient was used to evaluate the validity and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient was used to assess the reliability of WBB measures with respect to the FP. Classifiers based on Support Vector Machines trained on the FP and WBB features were used to assess the ability of both devices to discriminate between HS and MS.
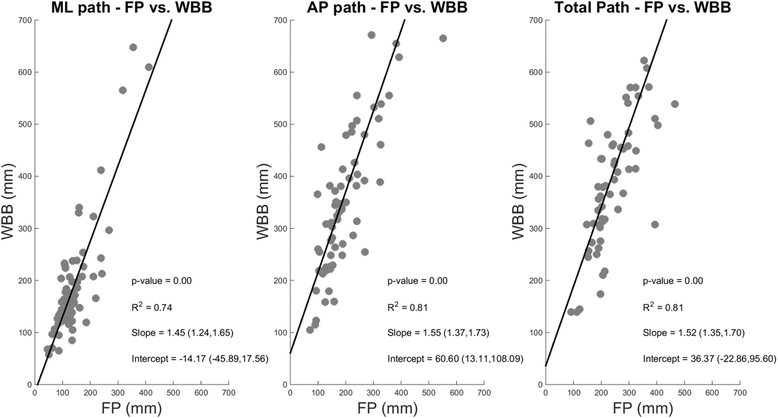
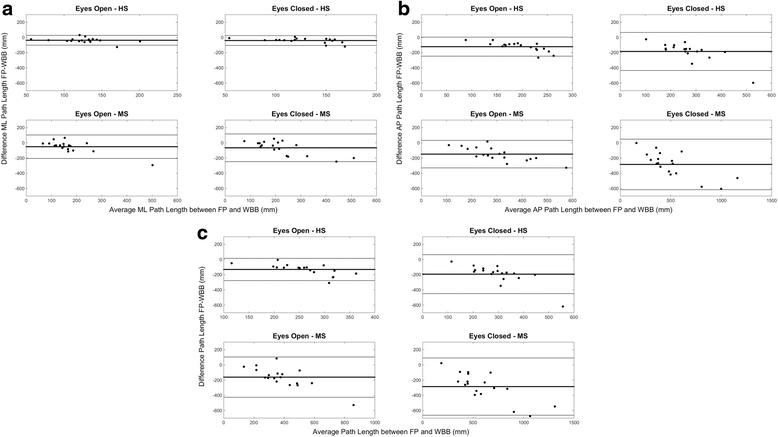
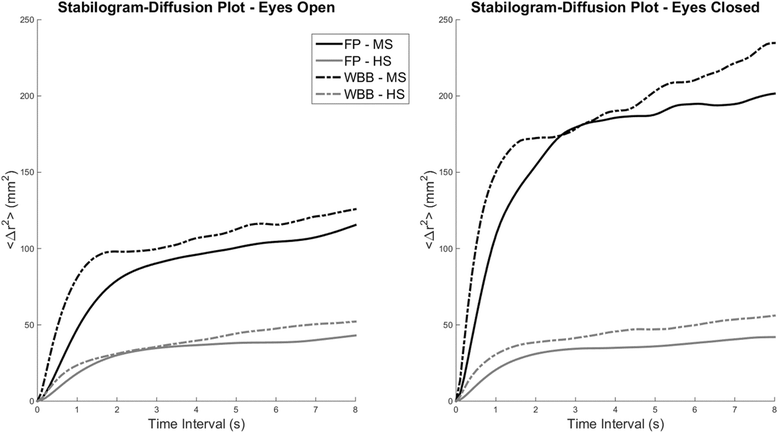
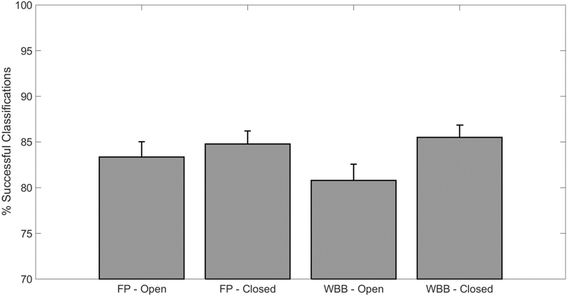
Results: We found a significant linear relation between the path lengths calculated from the WBB and the FP indicating an overestimation of these parameters in the WBB. We observed significant differences in the path lengths between FP and WBB in most conditions. However, significant differences were not found for the majority of the other features. We observed the same significant differences between the HS and MS populations across the two measurement systems. Validity and reliability were moderate-to-high for all the analyzed features. Both the FP and WBB trained classifier showed similar classification performance (>80%) when discriminating between HS and MS.
Conclusions: Our results support the observation that the WBB, although not suitable for obtaining absolute measures, could be successfully used in comparative analysis of different populations.
Keywords: Multiple Sclerosis; Posturographic Analysis; Wii Balance Board.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validity and reliability of the Nintendo Wii Balance Board for assessment of standing balance.Gait Posture. 2010 Mar;31(3):307-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2009.11.012. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Gait Posture. 2010. PMID: 20005112
-
Use of the Nintendo Wii Balance Board for Studying Standing Static Balance Control: Technical Considerations, Force-Plate Congruency, and the Effect of Battery Life.J Appl Biomech. 2017 Feb;33(1):48-55. doi: 10.1123/jab.2015-0295. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Appl Biomech. 2017. PMID: 27735224
-
Validity and reliability of balance assessment software using the Nintendo Wii balance board: usability and validation.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2014 Jun 10;11:99. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-11-99. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 24912769 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Synthesis of Nintendo Wii Fit Gaming Protocol in Addressing Balance Among Healthy Older Adults: What System Works?Games Health J. 2017 Apr;6(2):65-74. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2016.0082. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Games Health J. 2017. PMID: 28225644 Review.
-
Videonystagmography and Posturography.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;82:32-38. doi: 10.1159/000490269. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30947200 Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory Interaction and Balancing Ability Evaluation of the Elderly Using a Simplified Force Plate System.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;22(22):8883. doi: 10.3390/s22228883. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433479 Free PMC article.
-
The role of machine learning in developing non-magnetic resonance imaging based biomarkers for multiple sclerosis: a systematic review.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 Sep 15;22(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01985-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 36109726 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of a Low-Cost Gaming Platform as a Substitute to Medical-Grade Force Plate in Objective Evaluation of Balance.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Jun;74(2):217-224. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02963-5. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 35813771 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic data simultaneously acquired from dynamometric force plate and Nintendo Wii Balance Board during human static posture trials.Data Brief. 2019 Dec 19;28:105028. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.105028. eCollection 2020 Feb. Data Brief. 2019. PMID: 31909124 Free PMC article.
-
Mii-vitaliSe: a pilot randomised controlled trial of a home gaming system (Nintendo Wii) to increase activity levels, vitality and well-being in people with multiple sclerosis.BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 27;7(9):e016966. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016966. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28954791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Herrera WG. Vestibular and other balance disorders in multiple sclerosis. Differential diagnosis of disequilibrium and topognostic localization. Neurol Clin. 1990;8:407–20. - PubMed
-
- McAlpine D, Matthews WB. McAlpine’s Multiple Sclerosis. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK. 2nd ed. 1991.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

