Human IL-6RhiTIGIT- CD4+CD127lowCD25+ T cells display potent in vitro suppressive capacity and a distinct Th17 profile
- PMID: 28284938
- PMCID: PMC5471606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2017.03.002
Human IL-6RhiTIGIT- CD4+CD127lowCD25+ T cells display potent in vitro suppressive capacity and a distinct Th17 profile
Abstract
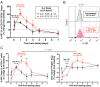
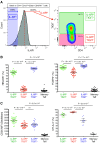
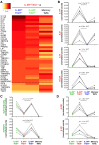
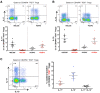
To date many clinical studies aim to increase the number and/or fitness of CD4+CD127lowCD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in vivo to harness their regulatory potential in the context of treating autoimmune disease. Here, we sought to define the phenotype and function of Tregs expressing the highest levels of IL-6 receptor (IL-6R). We have identified a population of CD4+CD127lowCD25+ TIGIT- T cells distinguished by their elevated IL-6R expression that lacked expression of HELIOS, showed higher CTLA-4 expression, and displayed increased suppressive capacity compared to IL-6RhiTIGIT+ Tregs. IL-6RhiTIGIT- CD127lowCD25+ T cells contained a majority of cells demethylated at FOXP3 and displayed a Th17 transcriptional signature, including RORC (RORγt) and the capacity of producing both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-17, IL-22 and IL-10. We propose that in vivo, in the presence of IL-6-associated inflammation, the suppressive function of CD4+CD127lowCD25+ FOXP3+IL-6RhiTIGIT- T cells is temporarily disarmed allowing further activation of the effector functions and potential pathogenic tissue damage.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Kitagawa Y., Ohkura N., Sakaguchi S. Epigenetic control of thymic Treg-cell development. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015;45:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Huehn J., Polansky J.K., Hamann A. Epigenetic control of FOXP3 expression: the key to a stable regulatory T-cell lineage? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009;9:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Yamanouchi J., Rainbow D., Serra P., Howlett S., Hunter K., Garner V.E.S., Gonzalez-Munoz A., Clark J., Veijola R., Cubbon R., Chen S.-L., Rosa R., Cumiskey A.M., Serreze D.V., Gregory S., Rogers J., Lyons P.A., Healy B., Smink L.J., Todd J.A., Peterson L.B., Wicker L.S., Santamaria P. Interleukin-2 gene variation impairs regulatory T cell function and causes autoimmunity. Nat Genet. 2007;39:329–337. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

