Canagliflozin as an Initial Therapy in Drug-Naïve Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Potential Involvement of Atherogenic Lipids in its Glycemic Efficacy
- PMID: 28285448
- PMCID: PMC5427050
- DOI: 10.1007/s40268-017-0179-7
Canagliflozin as an Initial Therapy in Drug-Naïve Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Potential Involvement of Atherogenic Lipids in its Glycemic Efficacy
Abstract
Background and objectives: The aim of this study is to investigate canagliflozin as an initial therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and to explore the effects on metabolic parameters in relation to effects on glycemic control.
Subjects and methods: Treatment-naïve subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus received canagliflozin 50-100 mg/day monotherapy. At 3 months, levels of glycemic and non-glycemic parameters were compared with those at baseline (n = 39). As a comparator, our previous data of baseline glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)-matched treatment-naïve subjects with ipragliflozin 25-50 mg monotherapy (n = 27) were employed.
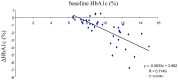
Results: Significant reductions in HbA1c (from 9.96 to 8.33%), fasting blood glucose (-23.9%), homeostasis model assessment-R (HOMA-R, -33.5%), body mass index (-1.8%), and uric acid (UA, -5.2%) levels and significant increases in homeostasis model assessment-B (HOMA-B, 30.1%) levels were observed. Approximately one third of the subjects experienced certain adverse events. Similar results were obtained with ipragliflozin. Baseline levels of HbA1c, triglycerides, non-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) were chosen as significant contributing factors for the changes in HbA1c levels with canagliflzoin, while only baseline HbA1c levels were selected as such a factor with ipragliflozin. Significant positive correlations between the changes in HbA1c and changes in non-HDL-C (R = 0.3954) or between changes in HbA1c and changes in LDL-C (R = 0.4317) were observed with canagliflozin. With ipragliflozin, no such correlations were noted. No correlations between the changes in HbA1c and changes in body mass index were seen with both drugs.
Conclusions: These results suggest that (1) canagliflozin appears to offer clinically beneficial outcomes as an initial therapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus, although with certain adverse events. (2) Atherogenic cholesterols including non-HDL-C and LDL-C could be involved in the glycemic efficacy of canagliflozin. This was not the case with ipragliflozin. (3) Unexpectedly, weight reductions with canagliflozin are not associated with its glycemic efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
No funding was received for the preparation and conduct of this study.
Conflict of interest
Eiji Kutoh, Asuka Wada, Teruma Murayama, and Yui Takizawa have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this study.
Ethics approval
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Conference on Harmonisation Good Clinical Practice guidelines.
Consent to participate
All subjects provided informed consent.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous