Hedgehog Signaling: From Basic Biology to Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 28286127
- PMCID: PMC7442121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.02.010
Hedgehog Signaling: From Basic Biology to Cancer Therapy
Abstract
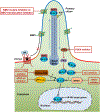
The Hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway was discovered originally as a key pathway in embryonic patterning and development. Since its discovery, it has become increasingly clear that the HH pathway also plays important roles in a multitude of cancers. Therefore, HH signaling has emerged as a therapeutic target of interest for cancer therapy. In this review, we provide a brief overview of HH signaling and the key molecular players involved and offer an up-to-date summary of our current knowledge of endogenous and exogenous small molecules that modulate HH signaling. We discuss experiences and lessons learned from the decades-long efforts toward the development of cancer therapies targeting the HH pathway. Challenges to develop next-generation cancer therapies are highlighted.
Keywords: GLI; basal cell carcinoma; cancer therapy; cholesterol; drug resistance; endogenous smoothened regulation; hedgehog signaling; medulloblastoma; smoothened; stem cell.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Adolphe C, Hetherington R, Ellis T, and Wainwright B (2006). Patched1 functions as a gatekeeper by promoting cell cycle progression. Cancer Res. 66, 2081–2088. - PubMed
-
- Amakye D, Robinson D, Rose K, Cho J, Ligon KL, Sharp T, Haider A, Bandaru R, Ando Y, Geoerger B, et al. (2012). Abstract 4818: the predictive value of a 5-gene signature as a patient pre-selection tool in medulloblastoma for Hedgehog pathway inhibitor therapy. Cancer Res. 72, 4818. - PubMed
-
- Amakye D, Jagani Z, and Dorsch M (2013). Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat. Med 19, 1410–1422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

