Development and characterization of a round hand-held silicon photomultiplier based gamma camera for intraoperative imaging
- PMID: 28286345
- PMCID: PMC5344198
- DOI: 10.1109/TNS.2014.2308284
Development and characterization of a round hand-held silicon photomultiplier based gamma camera for intraoperative imaging
Abstract
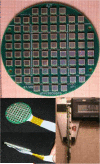
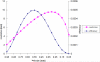
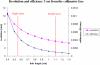
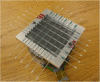
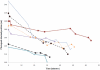
This paper describes the development of a hand-held gamma camera for intraoperative surgical guidance that is based on silicon photomultiplier (SiPM) technology. The camera incorporates a cerium doped lanthanum bromide (LaBr3:Ce) plate scintillator, an array of 80 SiPM photodetectors and a two-layer parallel-hole collimator. The field of view is circular with a 60 mm diameter. The disk-shaped camera housing is 75 mm in diameter, approximately 40.5 mm thick and has a mass of only 1.4 kg, permitting either hand-held or arm-mounted use. All camera components are integrated on a mobile cart that allows easy transport. The camera was developed for use in surgical procedures including determination of the location and extent of primary carcinomas, detection of secondary lesions and sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). Here we describe the camera design and its principal operating characteristics, including spatial resolution, energy resolution, sensitivity uniformity, and geometric linearity. The gamma camera has an intrinsic spatial resolution of 4.2 mm FWHM, an energy resolution of 21.1 % FWHM at 140 keV, and a sensitivity of 481 and 73 cps/MBq when using the single- and double-layer collimators, respectively.
Keywords: Biomedical imaging; Gamma-ray detectors; Instrumentation and measurement.
Figures









References
-
- Stoffels I, Poeppel T, Boy C, Mueller S, Wichmann F, Dissemond J, Schadendorf D, Rosenbaum-Krumme S, Klode J. Radio-guided surgery: advantages of a new portable γ-camera (Sentinella®) for intraoperative real time imaging and detection of sentinel lymph nodes in cutaneous malignancies. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2012;26(3):308–313. - PubMed
-
- Kerrou K, Pitre S, Coutant C, Rouzier R, Ancel PY, Lebeaux C, Huchet V, Montravers F, Pascal O, Duval MA, Lefebvre F, Menard L, Uzan S, Charon Y, Barranger E. The usefulness of a preoperative compact imager, a handheld γ-camera for breast cancer sentinel node biopsy: final results of a prospective double-blind, clinical study. The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2011;52(9):1346–1353. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DL, Olcott PD, Prat G, Levin CS. Novel handheld intraoperative radionuclide imaging. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 2010;17(supp. 1):S106–S107.
-
- Garbay J, Ricard M, Lumbroso J, Rimareix F, Uzan C, Gouy S, Leroy P. A new hand-held gamma camera for sentinel node detection in breast cancer. The Minicam e perience in 50 cases. Cancer Research. 2009;69(2, suppl.):1021.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
