Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy on Osteoclasts Precursors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 28286757
- PMCID: PMC5327780
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2690402
Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy on Osteoclasts Precursors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
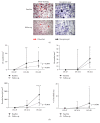
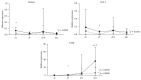
Objective. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) increases circulating osteoclast (OC) precursors numbers by promoting their proliferation and differentiation. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of TNF inhibitors (TNFi) on the differentiation and activity of OC in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Methods. Seventeen RA patients treated with TNFi were analyzed at baseline and after a minimum follow-up period of 6 months. Blood samples were collected to assess receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) surface expression on circulating leukocytes and frequency and phenotype of monocyte subpopulations. Quantification of serum levels of bone turnover markers, in vitro OC differentiation assays, and qRT-PCR for OC specific genes was performed. Results. After TNFi therapy, patients had reduced RANKL surface expression in B-lymphocytes and the frequency of circulating classical CD14brightCD16- monocytes was decreased. Serum levels of sRANKL, sRANKL/OPG ratio, and CTX-I were reduced in RA patients after TNFi treatment. Moreover, after exposure to TNFi, osteoclast differentiation and activity were decreased, as well as the expression of TRAF6 and cathepsin K. Conclusion. We propose that TNFi arrests bone loss and erosion, through two pathways: direct reduction of osteoclast precursor numbers and inhibition of intracellular signaling pathways acting through TRAF6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Appel H., Loddenkemper C., Miossec P. Rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis—pathology of acute inflammation. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2009;27(4, supplement 55):S15–S19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

