Radiation dose reduction: comparative assessment of publication volume between interventional and diagnostic radiology
- PMID: 28287072
- PMCID: PMC5411004
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2016.16196
Radiation dose reduction: comparative assessment of publication volume between interventional and diagnostic radiology
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to quantify and compare awareness regarding radiation dose reduction within the interventional radiology and diagnostic radiology communities.
Methods: Abstracts accepted to the annual meetings of the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR), the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE), the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), and the European Congress of Radiology (ECR) between 2005 and 2015 were analyzed using the search terms "interventional/computed tomography" and "radiation dose/radiation dose reduction." A PubMed query using the above-mentioned search terms for the years of 2005-2015 was performed.
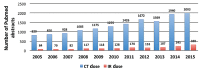
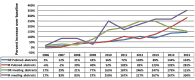
Results: Between 2005 and 2015, a total of 14 520 abstracts (mean, 660±297 abstracts) and 80 614 abstracts (mean, 3664±1025 abstracts) were presented at interventional and diagnostic radiology meetings, respectively. Significantly fewer abstracts related to radiation dose were presented at the interventional radiology meetings compared with the diagnostic radiology meetings (162 abstracts [1% of total] vs. 2706 [3% of total]; P < 0.001). On average 15±7 interventional radiology abstracts (range, 6-27) and 246±105 diagnostic radiology abstracts (range, 112-389) pertaining to radiation dose were presented at each meeting. The PubMed query revealed an average of 124±39 publications (range, 79-187) and 1205±307 publications (range, 829-1672) related to interventional and diagnostic radiology dose reduction per year, respectively (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The observed increase in the number of abstracts regarding radiation dose reduction in the interventional radiology community over the past 10 years has not mirrored the increased volume seen within diagnostic radiology, suggesting that increased education and discussion about this topic may be warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Publication rates for abstracts presented by Korean investigators at major radiology meetings.Korean J Radiol. 2008 Jul-Aug;9(4):303-11. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.4.303. Korean J Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18682667 Free PMC article.
-
[Structure of the meeting of the german radiological society and scientific discourse pertaining to radiation dose and dose reduction: an analysis of 1998 - 2008].Rofo. 2009 Nov;181(11):1065-72. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109818. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Rofo. 2009. PMID: 19830643 German.
-
Analysis of subsequent publication of scientific orally presented abstracts of the French national congress of radiology. Part I: General characteristics.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015 May;96(5):461-6. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25746222
-
Medical exposure to radiation and thyroid cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011 May;23(4):244-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2011.01.159. Epub 2011 Feb 5. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011. PMID: 21296564 Review.
-
Pediatric interventional radiology and dose-reduction techniques.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2014 Aug;35(4):409-14. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 28. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2014. PMID: 25129217 Review.
Cited by
-
Patient radiation dose during angiography and embolization for abdominal hemorrhage: the influence of CT angiography, fluoroscopy system, patient and procedural variables.CVIR Endovasc. 2022 Feb 16;5(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s42155-022-00284-4. CVIR Endovasc. 2022. PMID: 35171363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mettler FA, Jr, Bhargavan M, Faulkner K, et al. Radiologic and nuclear medicine studies in the United States and worldwide: frequency, radiation dose, and comparison with other radiation sources--1950–2007. Radiology. 2009;253:520–531. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2532082010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cardella JF, Miller DL, Cole PE, Lewis CA. Society of Interventional Radiology position statement on radiation safety. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14:S387. - PubMed
-
- Molinari F, Tack DM, Boiselle P, et al. Radiation dose management in thoracic CT: an international survey. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2277–2284. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra072149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith-Bindman R, Lipson J, Marcus R, et al. Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:2078–2086. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

