Plumbagin sensitizes breast cancer cells to tamoxifen-induced cell death through GRP78 inhibition and Bik upregulation
- PMID: 28287102
- PMCID: PMC5347125
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43781
Plumbagin sensitizes breast cancer cells to tamoxifen-induced cell death through GRP78 inhibition and Bik upregulation
Abstract
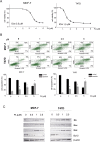
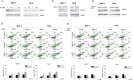
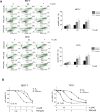
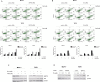
The glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is a major chaperone of the endoplasmic reticulum, and a prosurvival component of the unfolded protein response. GRP78 is upregulated in many types of cancers, including breast cancer. Research has suggested that GRP78 overexpression confers chemoresistance to anti-estrogen agents through a mechanism involving the inhibition of a pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein, Bik. In the present research the role of plumbagin, a naturally occurring naphthoquinone, in GRP78-associated cell death inhibition was examined. The results demonstrated that plumbagin inhibits GRP78 activity and GRP78 inhibition contributes to plumbagin-mediated cell death induction. Furthermore, Bik upregulation was associated with plumbagin-induced cell death and an increase in plumbagin-mediated Bik induction was observed upon GRP78 downregulation. Plumbagin sensitized estrogen-positive breast cancer cells to tamoxifen and the association of GRP78 inhibition and Bik upregulation in plumbagin-mediated cell sensitization was shown. Collectively, the results of this research suggest that plumbagin inhibits the antiapoptotic activity of GRP78 leading to Bik upregulation and apoptosis induction, which contributes to the sensitization of breast cancer cells to tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GRP78/BiP inhibits endoplasmic reticulum BIK and protects human breast cancer cells against estrogen starvation-induced apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 15;67(8):3734-40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4594. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17440086
-
Novel mechanism of anti-apoptotic function of 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78): endocrine resistance factor in breast cancer, through release of B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) from BCL-2-interacting killer (BIK).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25687-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212944. Epub 2011 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622563 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of the death gene BIK is a critical factor for resistance to tamoxifen in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2013 Dec;43(6):1777-86. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2127. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24100375 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of plumbagin: Cytotoxic potential and pharmaceutical relevance towards cancer therapy.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Mar;125:566-582. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.018. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30685472 Review.
-
Plumbagin: A Potential Anti-cancer Compound.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):731-737. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201116144421. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33200707 Review.
Cited by
-
Compensatory increases of select proteostasis networks after Hsp70 inhibition in cancer cells.J Cell Sci. 2018 Sep 5;131(17):jcs217760. doi: 10.1242/jcs.217760. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 30131440 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin relieves rheumatoid arthritis through nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13632-13642. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2081756. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35653787 Free PMC article.
-
3-Chloroplumbagin Induces Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cells Through MAPK-Mediated Mcl-1 Inhibition.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 26;10:784. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00784. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31404252 Free PMC article.
-
PaccMannRL: De novo generation of hit-like anticancer molecules from transcriptomic data via reinforcement learning.iScience. 2021 Mar 5;24(4):102269. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102269. eCollection 2021 Apr 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 33851095 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic cell death in colorectal cancer: a review of mechanisms and clinical utility.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Feb 14;73(3):53. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03641-5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38353760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clarke R., Leonessa F., Welch J. N. & Skaar T. C. Cellular and molecular pharmacology of antiestrogen action and resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 25–71 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Dalmau E., Armengol-Alonso A., Muñoz M. & Seguí-Palmer M. Á. Current status of hormone therapy in patients with hormone receptor positive (HR+) advanced breast cancer. Breast 23, 710–20 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Lee A. S. GRP78 induction in cancer: therapeutic and prognostic implications. Cancer Res. 67, 3496–9 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Lee A. S. The ER chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Methods 35, 373–81 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

