Killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteritidis and neutralization of lipopolysaccharide by 17-residue bovine lactoferricins: improved activity of Trp/Ala-containing molecules
- PMID: 28287172
- PMCID: PMC5347165
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44278
Killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteritidis and neutralization of lipopolysaccharide by 17-residue bovine lactoferricins: improved activity of Trp/Ala-containing molecules
Abstract
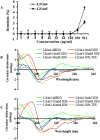
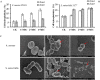
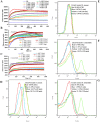
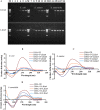
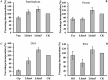
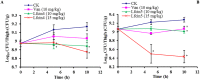
Bovine lactoferricin (LfcinB) has potent antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic activities but is also hemolytic. Our objective was to identify LfcinB17-31 derivatives with reduced hemolysis and improved antimicrobial activity via substituting Cys3, Arg4, Gln7, Met10, and Gly14 with more hydrophobic residues. Two peptides, Lfcin4 and Lfcin5, showed higher activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella enteritidis and lower hemolytic activity than the parent peptide LfcinB17-31. These peptides permeabilized the outer and inner membranes of S. enteritidis; however, Lfcin5 did not permeabilize the inner membrane of S. aureus. Gel retardation and circular dichroism spectra showed that Lfcin4 and Lfcin5 bound to bacterial genomic DNA. Lfcin4 inhibited DNA, RNA and protein synthesis. Both peptides induced the peeling of membranes and the lysis of S. enteritidis. At doses of 10 and 15 mg/kg, Lfcin4 and Lfcin5 reduced the bacterial counts in infected thigh muscles by 0.03‒0.10 and 0.05‒0.63 log10 CFU/g of tissue, respectively, within 10 h. Lfcin4 and Lfcin5 enhanced the survival rate of endotoxemic mice; reduced serum IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α levels; and protected mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. These data suggest that Lfcin4 and Lfcin5 may be antimicrobial and anti-endotoxin peptides that could serve as the basis for the development of dual-function agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity of 15-residue lactoferricin derivatives.J Pept Res. 2000 Nov;56(5):265-74. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3011.2000.00770.x. J Pept Res. 2000. PMID: 11095180
-
Antibacterial and detoxifying activity of NZ17074 analogues with multi-layers of selective antimicrobial actions against Escherichia coli and Salmonella enteritidis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 13;7(1):3392. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03664-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28611436 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of a 2-arylsulphonylated tryptophan: the antibacterial activity of bovine lactoferricin peptides containing Trp(2-Pmc).J Pept Sci. 2002 Jul;8(7):307-13. doi: 10.1002/psc.404. J Pept Sci. 2002. PMID: 12148780
-
Important structural features of 15-residue lactoferricin derivatives and methods for improvement of antimicrobial activity.Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;80(1):65-74. doi: 10.1139/o01-236. Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11908644 Review.
-
Towards a structure-function analysis of bovine lactoferricin and related tryptophan- and arginine-containing peptides.Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;80(1):49-63. doi: 10.1139/o01-213. Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11908643 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Activities of Lactoferrins, Lactoferricins, and Other Lactoferrin-Derived Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 19;22(20):11264. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011264. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary Structural Transformation of Bovine Lactoferricin Affects Its Antibacterial Activity.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021 Jun;13(3):873-884. doi: 10.1007/s12602-020-09726-8. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021. PMID: 33188636
-
Dual Antibacterial Activities and Biofilm Eradication of a Marine Peptide-N6NH2 and Its Analogs against Multidrug-Resistant Aeromonas veronii.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 17;21(24):9637. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249637. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33348848 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Pharmacodynamics of Recombinant Fungus Defensin NZL with Improved Activity against Staphylococcus hyicus In Vitro and In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5435. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115435. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34063982 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of NZ2114 against Streptococcus dysgalactiae biofilms and its application in murine mastitis model.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 15;13:1010148. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1010148. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36187987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diekema D. J. et al.. Survey of infections due to Staphylococcus species: frequency of occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates collected in the United States, Canada, Latin America, Europe, and the Western Pacific region for the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 1997-1999. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32 Suppl 2, S114–S132 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Wang Z., Cao B., Liu Y. M., Gu L. & Wang C. Investigation of the prevalence of patients co-colonized or infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin- resistant enterococci in China: a hospital-based study. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 122, 1283–1288 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lu Q. et al.. Pathogen and antimicrobial resistance profiles of culture-proven neonatal sepsis in Southwest China, 1990-2014. J. Paediatr. Child Health 52, 939–943 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

