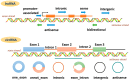
The Role and Molecular Mechanism of Non-Coding RNAs in Pathological Cardiac Remodeling
- PMID: 28287427
- PMCID: PMC5372624
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18030608
The Role and Molecular Mechanism of Non-Coding RNAs in Pathological Cardiac Remodeling
Abstract
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a class of RNA molecules that do not encode proteins. Studies show that ncRNAs are not only involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, metabolism and other physiological processes, but also involved in the pathogenesis of diseases. Cardiac remodeling is the main pathological basis of a variety of cardiovascular diseases. Many studies have shown that the occurrence and development of cardiac remodeling are closely related with the regulation of ncRNAs. Recent research of ncRNAs in heart disease has achieved rapid development. Thus, we summarize here the latest research progress and mainly the molecular mechanism of ncRNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), in cardiac remodeling, aiming to look for new targets for heart disease treatment.
Keywords: cardiac remodeling; circular RNA; long non-coding RNA; microRNA; non-coding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA/circular noncoding RNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in cardiovascular diseases.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 15;233:116440. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.066. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31047893 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs and angiogenesis in cardiovascular diseases: a comprehensive review.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Nov;479(11):2921-2953. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04919-5. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38306012 Review.
-
Noncoding RNA as regulators of cardiac fibrosis: current insight and the road ahead.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jun;468(6):1103-11. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1792-y. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26786602 Review.
-
[Non-coding RNA : Innovative regulators with therapeutic perspective].Herz. 2018 Mar;43(2):115-122. doi: 10.1007/s00059-017-4660-4. Herz. 2018. PMID: 29236145 Review. German.
-
Involvement of Non-coding RNAs in the Signaling Pathways of Colorectal Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:19-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27573893 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network and Crucial Signaling Pathway Axis Involved in Tetralogy of Fallot.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 7;13:917454. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.917454. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35873466 Free PMC article.
-
Functional predication of differentially expressed circRNAs/lncRNAs in the prefrontal cortex of Nrf2-knockout mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 10;13(6):8797-8816. doi: 10.18632/aging.202688. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33714958 Free PMC article.
-
The Lnc LINC00461/miR-30a-5p facilitates progression and malignancy in non-small cell lung cancer via regulating ZEB2.Cell Cycle. 2020 Apr;19(7):825-836. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1731946. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Cell Cycle. 2020. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2023 Mar-Mar;22(6):736. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2171196. PMID: 32106756 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Autophagy in cardiovascular diseases: role of noncoding RNAs.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Nov 4;23:101-118. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.039. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 33335796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of circRNA DMNT3B contributes to diabetic retinal vascular dysfunction through targeting miR-20b-5p and BAMBI.EBioMedicine. 2019 Nov;49:341-353. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Oct 19. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31636010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rinn J.L., Kertesz M., Wang J.K., Squazzo S.L., Xu X., Brugmann S.A., Goodnough L.H., Helms J.A., Farnham P.J., Segal E., et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129:1311–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources