Regulating miRNA-21 Biogenesis By Bifunctional Small Molecules
- PMID: 28287718
- PMCID: PMC5620130
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b00610
Regulating miRNA-21 Biogenesis By Bifunctional Small Molecules
Abstract
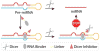
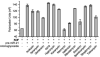
We report a new strategy to regulate microRNAs (miRNAs) biogenesis by using bifunctional small molecules that consist of a pre-miRNA binding unit connected by a linker to a Dicer inhibiting unit. In this effort, fluorescence polarization-based screening was used to identify neomycin as a pre-miR-21 binding ligand. Although neomycin cannot inhibit miR-21 maturation, linking it to the RNase inhibitor 1 forms the bifunctional conjugate 7A, which inhibits the production of miR-21. We expect that this strategy will be applicable to design other molecules for miRNA regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
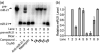
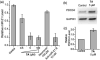
Similar articles
-
Bifunctional small molecule-oligonucleotide hybrid as microRNA inhibitor.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Apr 1;28(7):115394. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115394. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32139203 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and activity of light deactivatable microRNA inhibitor.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Oct;80:492-497. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29990897 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the production of oncogenic microRNAs with multimodal synthetic small molecules.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Mar 21;9(3):711-21. doi: 10.1021/cb400668h. Epub 2014 Jan 3. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24359019
-
Re-evaluation of the roles of DROSHA, Export in 5, and DICER in microRNA biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 29;113(13):E1881-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602532113. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26976605 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing factors as regulators of miRNA biogenesis - links to human disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Jul;79:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29042235 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of MicroRNAs by Coupling Cyclic Enzymatic Amplification with Microfluidic Voltage-Assisted Liquid Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2018 Nov 20;90(22):13663-13669. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04008. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 30359531 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MicroRNAs with Small Molecules.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Mar 14;10(2):17. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10020017. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38525736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interbase-FRET binding assay for pre-microRNAs.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;11(1):9396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88922-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33931703 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules with big roles in microRNA chemical biology and microRNA-targeted therapeutics.RNA Biol. 2019 Jun;16(6):707-718. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1593094. Epub 2019 Apr 3. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 30900502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ribonucleases with Small Molecules and Bifunctional Molecules.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Oct 20;18(10):2101-2113. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00191. Epub 2023 Jun 29. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37382390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ameres SL, Zamore PD. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;14:475. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

