The Asthma Mobile Health Study, a large-scale clinical observational study using ResearchKit
- PMID: 28288104
- PMCID: PMC5559298
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3826
The Asthma Mobile Health Study, a large-scale clinical observational study using ResearchKit
Abstract
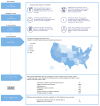
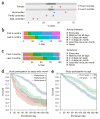
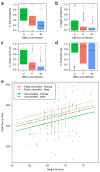
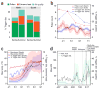
The feasibility of using mobile health applications to conduct observational clinical studies requires rigorous validation. Here, we report initial findings from the Asthma Mobile Health Study, a research study, including recruitment, consent, and enrollment, conducted entirely remotely by smartphone. We achieved secure bidirectional data flow between investigators and 7,593 participants from across the United States, including many with severe asthma. Our platform enabled prospective collection of longitudinal, multidimensional data (e.g., surveys, devices, geolocation, and air quality) in a subset of users over the 6-month study period. Consistent trending and correlation of interrelated variables support the quality of data obtained via this method. We detected increased reporting of asthma symptoms in regions affected by heat, pollen, and wildfires. Potential challenges with this technology include selection bias, low retention rates, reporting bias, and data security. These issues require attention to realize the full potential of mobile platforms in research and patient care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details are available in the online version of the paper.
Figures
Comment in
-
mHealth advances clinical research, bit by bit.Nat Biotechnol. 2017 Apr 11;35(4):337-339. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3851. Nat Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28398316 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ritter S. Apple’s research kit development framework for iPhone apps enables innovative approaches to medical research data collection. J Clin Trials. 2015;5:2–3.
-
- Morgan A, Mooney S, Aronow B, Brenner S. Precision Medicine: Data and Discovery for Improved Health and Therapy. [Accessed May 7, 2016];Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. 2016 http://psb.stanford.edu/psb-online/proceedings/psb16/intro-pm.pdf. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savage N. Mobile data: Made to measure. Nature. 2015;527:S12–S13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

