A multidisciplinary, integrated approach for the elimination of schistosomiasis: a longitudinal study in a historically hyper-endemic region in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China from 2005 to 2014
- PMID: 28288689
- PMCID: PMC5348877
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-017-0270-x
A multidisciplinary, integrated approach for the elimination of schistosomiasis: a longitudinal study in a historically hyper-endemic region in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China from 2005 to 2014
Abstract
Background: Although great success has been achieved, schistosomiasis remains a major public health concern in China, and the remaining core endemic regions are concentrated along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. In this longitudinal study, we evaluated the effectiveness of a multidisciplinary, integrated approach for schistosomiasis elimination in a historically hyper-endemic region in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China over the 10-year period from 2005 through 2014.
Methods: A three-step roadmap for schistosomiasis elimination was designed in the study site, and multidisciplinary, integrated interventions were implemented by the health, agriculture, water resources development, land and resources, and forestry sectors from 2005 to 2014, including chemotherapy for infected individuals, health education, management of the source of Schistosoma japonicum infection, and intermediate host snail control. The annual number of schistosomiasis patients, S. japonicum infection in humans, bovines and Oncomelania hupensis snails, and water infectivity were observed to assess the effectiveness of the multidisciplinary, integrated approach for the elimination of schistosomiasis.
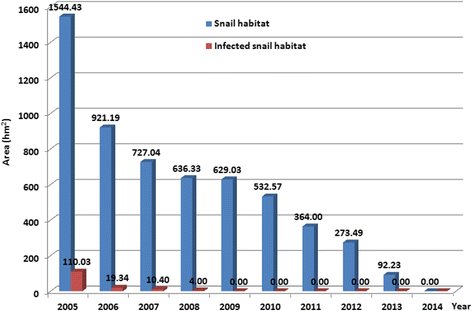
Results: There was a tendency towards a gradual decline in both the number of schistosomiasis cases and the prevalence of S. japonicum human infection across the study period from 2005 through 2014. No S. japonicum human infection was detected since 2012, and no acute infection was seen since 2006. During the study period, no infection was found in bovines, and a 0.03% overall infection rate was observed in O. hupensis snails. Since 2009, no infected snails were identified, and the area of both snail habitats and infected snail habitats appeared a reduction over the study period. Following the 3-year multidisciplinary, integrated control, infection control was achieved, and transmission control was achieved after 6-year implementation, with all infected snails and water infectivity eliminated; in addition, the 10-year implementation resulted in interruption of schistosomiasis transmission in the study site in 2014.
Conclusions: The results of the present 10-year longitudinal study demonstrate that the multidisciplinary, integrated approach is effective for the elimination of schistosomiasis as a public health problem in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China.
Keywords: China; Elimination; Integrated control; Longitudinal study; Multidisciplinary approach; Schistosomiasis; Yangtze River.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Interruption of schistosomiasis transmission in mountainous and hilly regions with an integrated strategy: a longitudinal case study in Sichuan, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Apr 7;6(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0290-6. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28385163 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated environmental improvement of marshlands: impact on control and elimination of schistosomiasis in marshland regions along the Yangtze River, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Mar 22;6(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0287-1. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28330510 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectiveness of the integrated schistosomiasis control programme in Wuhan City from 2005 to 2023].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 21;37(2):176-183. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1915.2024200. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40425500 Chinese.
-
Approaches being used in the national schistosomiasis elimination programme in China: a review.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Mar 15;6(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0271-9. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28292327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Three Gorges Dam: Does it accelerate or delay the progress towards eliminating transmission of schistosomiasis in China?Infect Dis Poverty. 2016 Jul 5;5(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0156-3. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016. PMID: 27377962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neglected tropical diseases: an effective global response to local poverty-related disease priorities.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Jan 28;9(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-0630-9. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 31987053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Core components, concepts and strategies for parasitic and vector-borne disease elimination with a focus on schistosomiasis: A landscape analysis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Oct 30;14(10):e0008837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008837. eCollection 2020 Oct. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 33125375 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes and practices related to schistosomiasis transmission and control in Leyte, Philippines.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 May 2;13(5):e0007358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007358. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31048882 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal transcriptome change of Oncomelania hupensis revealed by Schistosoma japonicum invasion.Cell Biosci. 2020 Apr 17;10:58. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00420-4. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32328235 Free PMC article.
-
SWOT analysis on snail control measures applied in the national schistosomiasis control programme in the People's Republic of China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2019 Feb 6;8(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40249-019-0521-0. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019. PMID: 30732636 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

