China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial: Visit-to-Visit Systolic Blood Pressure Variability Is an Independent Predictor of Primary Stroke in Hypertensive Patients
- PMID: 28288974
- PMCID: PMC5523997
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004350
China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial: Visit-to-Visit Systolic Blood Pressure Variability Is an Independent Predictor of Primary Stroke in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
Background: The optimal range of blood pressure variability remains unclear. We aimed to stratify the degree of risk of stroke based on visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure (SBP) variability in a large Chinese hypertensive population in 32 communities.
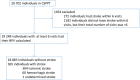
Methods and results: We retrospectively analyzed the data of 20 702 hypertensive patients from the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial. The participants were randomized into 2 treatment groups to receive either enalapril or enalapril plus folic acid. Their blood pressures were measured every 3 months. The outcome was the first stroke. Three parameters of SBP variability were calculated: standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and average real variability. The records of first 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12 visits at which SBP was measured were used to calculate SBP variability and to predict subsequent stroke risk in adjusted Cox regression models. After median follow-up of 4.5 years, 597 patients had experienced stroke. Visit-to-visit SBP variability was an independent predictor of subsequent stroke (eg, the hazard ratio for the highest quintile of average real variability [22.67-61.07 mm Hg] over 6 visits was 1.55, 95% CI 1.07-2.25, P=0.021), independent of mean SBP over the follow-up period. Its value was more predictive when more blood pressure records were used.
Conclusions: Visit-to-visit SBP variability is an independent predictor of primary stroke in Chinese hypertensive patients. This predictive value depends on the number of blood pressure measurements used to calculate variability but is independent of mean SBP.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00794885.
Keywords: hypertension; stroke; systolic blood pressure variability.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Charles W, Cathie S, Martin D, Joanna W, Peter S. Stroke. Lancet. 2003;362:1211–1224.
-
- Lawes CMM, Hoorn SV, Rodgers A; For the International Society of Hypertension . Global burden of blood‐pressure‐related disease, 2001. Lancet. 2008;371:1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- WHO document . A global brief on hypertension. 2015. Available at http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_disease/publication/global_brief_hyper.... Accessed December 23, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

