Mapping Neurodegenerative Disease Onset and Progression
- PMID: 28289062
- PMCID: PMC5538416
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a023622
Mapping Neurodegenerative Disease Onset and Progression
Abstract
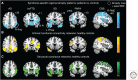
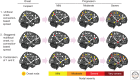
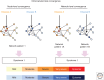
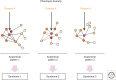
Brain networks have been of long-standing interest to neurodegeneration researchers, including but not limited to investigators focusing on conventional prion diseases, which are known to propagate along neural pathways. Tools for human network mapping, however, remained inadequate, limiting our understanding of human brain network architecture and preventing clinical research applications. Until recently, neuropathological studies were the only viable approach to mapping disease onset and progression in humans but required large autopsy cohorts and laborious methods for whole-brain sectioning and staining. Despite important advantages, postmortem studies cannot address in vivo, physiological, or longitudinal questions and have limited potential to explore early-stage disease except for the most common disorders. Emerging in vivo network-based neuroimaging strategies have begun to address these issues, providing data that complement the neuropathological tradition. Overall, findings to date highlight several fundamental principles of neurodegenerative disease anatomy and pathogenesis, as well as some enduring mysteries. These principles and mysteries provide a road map for future research.
Copyright © 2017 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Appel SH. 1981. A unifying hypothesis for the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, parkinsonism, and Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 10: 499–505. - PubMed
-
- Baker HF, Ridley RM, Duchen LW, Crow TJ, Bruton CJ. 1994. Induction of β (A4)-amyloid in primates by injection of Alzheimer's disease brain homogenate. Comparison with transmission of spongiform encephalopathy. Mol Neurobiol 8: 25–39. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. 1995. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34: 537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
