What Is Wrong with Pertussis Vaccine Immunity? The Problem of Waning Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccines
- PMID: 28289064
- PMCID: PMC5710106
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029454
What Is Wrong with Pertussis Vaccine Immunity? The Problem of Waning Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccines
Abstract
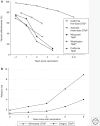
Pertussis is resurgent in some countries, particularly those in which children receive acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines in early infancy and boosters later in life. Immunologic studies show that, whereas whole-cell pertussis (wP) vaccines orient the immune system toward Th1/Th17 responses, acellular pertussis vaccines orient toward Th1/Th2 responses. Although aP vaccines do provide protection during the first years of life, the change in T-cell priming results in waning effectiveness of aP as early as 2-3 years post-boosters. Although other factors, such as increased virulence of pertussis strains, better diagnosis, and better surveillance may play a role, the increase in pertussis appears to be the result of waning immunity. In addition, studies in baboon models, requiring confirmation in humans, show that aP is less able to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization of Bordetella pertussis than wP or natural infection.
Copyright © 2017 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Allen AC, Mills KH. 2014. Improved pertussis vaccines based on adjuvants that induce cell-mediated immunity. Expert Rev Vaccines 13: 1253–1264. - PubMed
-
- Asensio CJ, Gaillard ME, Moreno G, Bottero D, Zurita E, Rumbo M, van der Ley P, van der Ark A, Hozbor D. 2011. Outer membrane vesicles obtained from Bordetella pertussis Tohama expressing the lipid A deacylase PagL as a novel acellular vaccine candidate. Vaccine 29: 1649–1656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
