Delivery is key: lessons learnt from developing splice-switching antisense therapies
- PMID: 28289078
- PMCID: PMC5412803
- DOI: 10.15252/emmm.201607199
Delivery is key: lessons learnt from developing splice-switching antisense therapies
Abstract
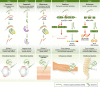
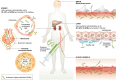
The use of splice-switching antisense therapy is highly promising, with a wealth of pre-clinical data and numerous clinical trials ongoing. Nevertheless, its potential to treat a variety of disorders has yet to be realized. The main obstacle impeding the clinical translation of this approach is the relatively poor delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to target tissues after systemic delivery. We are a group of researchers closely involved in the development of these therapies and would like to communicate our discussions concerning the validity of standard methodologies currently used in their pre-clinical development, the gaps in current knowledge and the pertinent challenges facing the field. We therefore make recommendations in order to focus future research efforts and facilitate a wider application of therapeutic antisense oligonucleotides.
Keywords: RNA therapy; antisense oligonucleotides; delivery; pre‐clinical models; toxicity.
© 2017 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures
References
-
- Aartsma‐Rus A, Janson AA, Kaman WE, Bremmer‐Bout M, den Dunnen JT, Baas F, van Ommen GJ, van Deutekom JC (2003) Therapeutic antisense‐induced exon skipping in cultured muscle cells from six different DMD patients. Hum Mol Genet 12: 907–914 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical