Proteome-wide Mapping of Endogenous SUMOylation Sites in Mouse Testis
- PMID: 28289178
- PMCID: PMC5417816
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M116.062125
Proteome-wide Mapping of Endogenous SUMOylation Sites in Mouse Testis
Abstract
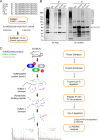
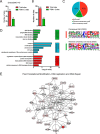
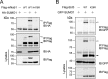
SUMOylation is a reversible post-translational modification involved in various critical biological processes. To date, there is limited approach for endogenous wild-type SUMO-modified peptides enrichment and SUMOylation sites identification. In this study, we generated a high-affinity SUMO1 antibody to facilitate the enrichment of endogenous SUMO1-modified peptides from Trypsin/Lys-C protease digestion. Following secondary Glu-C protease digestion, we identified 53 high-confidence SUMO1-modified sites from mouse testis by using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Bioinformatics analyses showed that SUMO1-modified proteins were enriched in transcription regulation and DNA repair. Nab1 was validated to be an authentic SUMOylated protein and Lys479 was identified to be the major SUMOylation site. The SUMOylation of Nab1 enhanced its interaction with HDAC2 and maintained its inhibitory effect on EGR1 transcriptional activity. Therefore, we provided a novel approach to investigating endogenous SUMOylation sites in tissue samples.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Geiss-Friedlander R., and Melchior F. (2007) Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 947–956 - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay D., and Dasso M. (2007) Modification in reverse: the SUMO proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 32, 286–295 - PubMed
-
- Hay R. T. (2005) SUMO: a history of modification. Mol. Cell 18, 1–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

