Phosphorylation-induced conformational dynamics in an intrinsically disordered protein and potential role in phenotypic heterogeneity
- PMID: 28289210
- PMCID: PMC5380051
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1700082114
Phosphorylation-induced conformational dynamics in an intrinsically disordered protein and potential role in phenotypic heterogeneity
Abstract
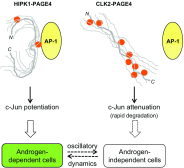
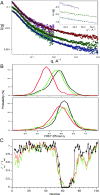
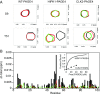
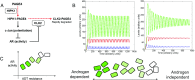
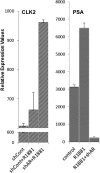
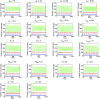
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) that lack a unique 3D structure and comprise a large fraction of the human proteome play important roles in numerous cellular functions. Prostate-Associated Gene 4 (PAGE4) is an IDP that acts as a potentiator of the Activator Protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factor. Homeodomain-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 (HIPK1) phosphorylates PAGE4 at S9 and T51, but only T51 is critical for its activity. Here, we identify a second kinase, CDC-Like Kinase 2 (CLK2), which acts on PAGE4 and hyperphosphorylates it at multiple S/T residues, including S9 and T51. We demonstrate that HIPK1 is expressed in both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer (PCa) cells, whereas CLK2 and PAGE4 are expressed only in androgen-dependent cells. Cell-based studies indicate that PAGE4 interaction with the two kinases leads to opposing functions. HIPK1-phosphorylated PAGE4 (HIPK1-PAGE4) potentiates c-Jun, whereas CLK2-phosphorylated PAGE4 (CLK2-PAGE4) attenuates c-Jun activity. Consistent with the cellular data, biophysical measurements (small-angle X-ray scattering, single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer, and NMR) indicate that HIPK1-PAGE4 exhibits a relatively compact conformational ensemble that binds AP-1, whereas CLK2-PAGE4 is more expanded and resembles a random coil with diminished affinity for AP-1. Taken together, the results suggest that the phosphorylation-induced conformational dynamics of PAGE4 may play a role in modulating changes between PCa cell phenotypes. A mathematical model based on our experimental data demonstrates how differential phosphorylation of PAGE4 can lead to transitions between androgen-dependent and androgen-independent phenotypes by altering the AP-1/androgen receptor regulatory circuit in PCa cells.
Keywords: PAGE-4; androgen resistance; intrinsic disorder; phenotypic heterogeneity; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Re: Phosphorylation-Induced Conformational Dynamics in an Intrinsically Disordered Protein and Potential Role in Phenotypic Heterogeneity.J Urol. 2017 Sep;198(3):486-487. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.06.013. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28817917 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anfinsen CB. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973;181(4096):223–230. - PubMed
-
- Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(3):197–208. - PubMed
-
- Oldfield CJ, Dunker AK. Intrinsically disordered proteins and intrinsically disordered protein regions. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:553–584. - PubMed
-
- Barabasi A-L. Scale-free networks: A decade and beyond. Science. 2009;325(5939):412–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

