Eosinophilic Esophagitis: an Emerging Clinicopathologic Disease of Children and Adults
- PMID: 28289340
- PMCID: PMC5338190
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: an Emerging Clinicopathologic Disease of Children and Adults
Abstract
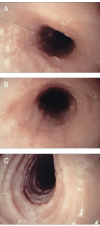
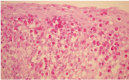
Eosinophililc esophagitis is a clinicopathologic disease characterized clinically by dysphagia and food impaction in adults and nonspecific symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease in children, and histologically by large numbers of eosinophils in the proximal and distal esophageal epithelium. Importantly, these symptoms and histologic abnormalities appear to be unresponsive to proton pump inhibition. Recent clinical and basic studies suggest an allergic etiology but the precise allergen remains unknown and is likely unique for each patient. Endoscopic features suggest ongoing inflammation and range from linear furrowing with whitish exudation to long-segment stricture formation, to a fragile, crepe paper-like mucosa that is easily split open. Treatments include nutritional restrictions, medical management with topical steroids, and, in stenotic circumstances, esophageal dilation. The long-term outcome is still not certain.
Keywords: Eosinophil; allergic esophagitis; dysphagia; esophageal stricture; food impaction; interleukin-5.
Figures
References
-
- Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis [letter] N Engl J Med. 2004;351:940–941. - PubMed
-
- Straumann A, Simon HU. Eosinophilic esophagitis—escalating epidemiology? [letter] J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:418–419. - PubMed
-
- Croese J, Fairley SK, Masson JW, et al. Clinical and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:516–522. - PubMed
-
- Arora AS, Yamazaki K. Eosinophilic esophagitis: asthma of the esophagus? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia, a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:109–116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
