Theabrownin Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression and Tumor Growth of Lung Carcinoma through c-myc-Related Mechanism
- PMID: 28289384
- PMCID: PMC5326752
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00075
Theabrownin Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression and Tumor Growth of Lung Carcinoma through c-myc-Related Mechanism
Abstract
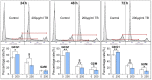
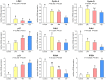
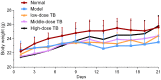
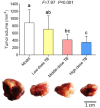
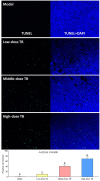
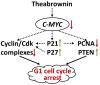
Green tea, the fresh leaves of Camellia sinensis, is not only a health-promoting beverage but also a traditional Chinese medicine used for prevention or treatment of cancer, such as lung cancer. Theabrownin (TB) is the main fraction responsible for the medicinal effects of green tea, but whether it possesses anti-cancer effect is unknown yet. This study aimed to determine the in vitro and in vivo anti-lung cancer effect of TB and explore the underlying molecular mechanism, by using A549 cell line and Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice. In cellular experiment, MTT assay was performed to evaluate the inhibitory effect and IC50 values of TB, and flow cytometry was conducted to analyze the cell cycle progression affected by TB. In animal experiment, mice body mass, tumor incidence, tumor size and tumor weight were measured, and histopathological analysis on tumor was performed with Transferase dUTP nick-end labeling staining. Real time PCR and western blot assays were adopted to detect the expression of C-MYC associated genes and proteins for mechanism clarification. TB was found to inhibit A549 cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner and block A549 cell cycle at G0/G1 phase. Down-regulation of c-myc, cyclin A, cyclin D, cdk2, cdk4, proliferation of cell nuclear antigen and up-regulation of p21, p27, and phosphate and tension homolog in both gene and protein levels were observed with TB treatment. A c-myc-related mechanism was thereby proposed, since c-myc could transcriptionally regulate all other genes in its downstream region for G1/S transitions of cell cycle and proliferation of cancer cells. This is the first report regarding the anti-NSCLC effect and the underlying mechanism of TB on cell cycle progression and proliferation of A549 cells. The in vivo data verified the in vitro result that TB could significantly inhibit the lung cancer growth in mice and induce apoptosis on tumors in a dose-dependent manner. It provides a promising candidate of natural products for lung cancer therapy and new development of anti-cancer agent.
Keywords: TUNEL; c-myc; cell cycle; lung cancer; theabrownin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-Proliferative and Apoptosis-Inducing Effect of Theabrownin against Non-small Cell Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Dec 2;7:465. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00465. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27994550 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea-derived theabrownin suppresses human non-small cell lung carcinoma in xenograft model through activation of not only p53 signaling but also MAPK/JNK signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 12;291:115167. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115167. Epub 2022 Mar 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35271947
-
Theabrownin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest of Oligodendroglioma and Astrocytoma in Different Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 30;12:664003. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.664003. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995088 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine Ze-Qi-Tang formula inhibit growth of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through the p53 pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Apr 24;234:180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30660711
-
Green tea-derived theabrownin induces cellular senescence and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through p53 signaling activation and bypassed JNK signaling suppression.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jan 25;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02468-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35078476 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Parthenolide enhances the metronomic chemotherapy effect of cyclophosphamide in lung cancer by inhibiting the NF-kB signaling pathway.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(7):895-907. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.895. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39071467 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoside Inhibits RNF8-mediated Nuclear Translocation of β-catenin to Repress PD-L1 Expression and Prostate Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(6):464-476. doi: 10.2174/0118715206289246240110044931. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38305391
-
Effect and mechanism of RNAi targeting WWTR1 on biological activity of gastric cancer cells SGC7901.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):2853-2860. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8192. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29207147 Free PMC article.
-
[Luteolin has a significant protective effect against cadmium-induced injury in lung epithelial Beas-2B cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 May 20;41(5):729-735. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.05.14. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34134961 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Theabrownins Produced via Chemical Oxidation of Tea Polyphenols Inhibit Human Lung Cancer Cells in vivo and in vitro by Suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Activation and Promoting Autophagy.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 21;9:858261. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.858261. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35529455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society (2016). Cancer Facts and Figures 2016. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

