Plant Derived Phytocompound, Embelin in CNS Disorders: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 28289385
- PMCID: PMC5326771
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00076
Plant Derived Phytocompound, Embelin in CNS Disorders: A Systematic Review
Abstract
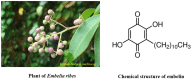
A Central nervous system (CNS) disease is the one which affects either the spinal cord or brain and causing neurological or psychiatric complications. During the nineteenth century, modern medicines have occupied the therapy for many ailments and are widely used these days. Herbal medicines have often maintained popularity for historical and cultural reasons and also considered safer as they originate from natural sources. Embelin is a plant-based benzoquinone which is the major active constituent of the fruits of Embelia ribes Burm. It is an Indo-Malaysian species, extensively used in various traditional medicine systems for treating various diseases. Several natural products including quinone derivatives, which are considered to possess better safety and efficacy profile, are known for their CNS related activity. The bright orange hydroxybenzoquinone embelin-rich fruits of E. ribes have become popular in ethnomedicine. The present systematic review summarizes the effects of embelin on central nervous system and related diseases. A PRISMA model for systematic review was utilized for search. Various electronic databases such as Pubmed, Springer, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar were searched between January 2000 and February 2016. Based on the search criteria for the literature, 13 qualified articles were selected and discussed in this review. The results of the report showed that there is a lack of translational research and not a single study was found in human. This report gives embelin a further way to be explored in clinical trials for its safety and efficacy.
Keywords: CNS disorders; embelin; natural product; neurodegenerative diseases; neuropharmacology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reviewing the Traditional/Modern Uses, Phytochemistry, Essential Oils/Extracts and Pharmacology of Embelia ribes Burm.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 13;11(7):1359. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071359. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of response surface methodology for optimization of extraction parameters and quantitative estimation of embelin from Embelia ribes Burm by high performance liquid chromatography.Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 May;11(Suppl 1):S166-72. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.157722. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015. PMID: 26109763 Free PMC article.
-
Embelin - a drug of antiquity: shifting the paradigm towards modern medicine.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Mar;23(3):427-44. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.867016. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24397264 Review.
-
Antipsychotic activity of embelin isolated from Embelia ribes: A preliminary study.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:328-331. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.085. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28376400
-
Chemical and Biological Aspects of the Natural 1,4-Benzoquinone Embelin and its (semi-)Synthetic Derivatives.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(18):1998-2009. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170116125731. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28093981 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut-brain axis and brain health: modulating neuroinflammation, cognitive decline, and neurodegeneration.3 Biotech. 2025 Jan;15(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04187-0. Epub 2024 Dec 27. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 39735610 Review.
-
A Review on Central Nervous System Effects of Gastrodin.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Feb 2;9:24. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00024. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29456504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Properties of Embelin in Cell Culture. Electrochemistry and Theoretical Mechanism of Scavenging. Potential Scavenging of Superoxide Radical through the Cell Membrane.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 May 5;9(5):382. doi: 10.3390/antiox9050382. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32380755 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Embelin in Benzo[α]pyrene induced cognitive and memory impairment in experimental model of mice.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2024 Jan 5;6:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100122. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38616958 Free PMC article.
-
6-(Ar)Alkylamino-Substituted Uracil Derivatives: Lipid Mimetics with Potent Activity at the Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor 84 (GPR84).ACS Omega. 2018 Mar 31;3(3):3365-3383. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b02092. Epub 2018 Mar 20. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 30023867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzal M., Gupta G., Kazmi I., Rahman M., Upadhyay G., Ahmad K., et al. (2012). Evaluation of anxiolytic activity of embelin isolated from Embelia ribes. Biomed. Aging Pathol. 2, 45–47. 10.1016/j.biomag.2012.03.003 - DOI
-
- Ahn K. S., Sethi G., Aggarwal B. B. (2007). Embelin, an inhibitor of X chromosome-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein, blocks nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway leading to suppression of NF-κB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene products. Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 209–219. 10.1124/mol.106.028787 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials