Genome sequence and description of Anaeromassilibacillus senegalensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gut of patient with kwashiorkor
- PMID: 28289546
- PMCID: PMC5338722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2017.01.009
Genome sequence and description of Anaeromassilibacillus senegalensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gut of patient with kwashiorkor
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Genome sequence and description of Anaeromassilibacillus senegalensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gut of patient with kwashiorkor.New Microbes New Infect. 2024 Apr 3;59:101313. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2024.101313. eCollection 2024 Jun. New Microbes New Infect. 2024. PMID: 38799818 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
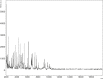
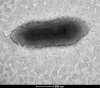
Using the culturomics strategy, a wide range of anaerobic bacteria was discovered including Anaeromassilibacillus senegalensis strain mt9T (= CSUR P1511 = DSM 102954), isolated from the gut microbiota of a 1-year-old Senegalese patient with kwashiorkor. This Gram-negative strain is a strictly anaerobic, spore-forming rod motile by a polar flagellum. The 3 511 289 bp long genome of this strain contains 3046 protein-coding and 49 RNA genes, including 45 tRNA and four rRNA genes, and exhibits a G+C content of 52.94%. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence and annotation.
Keywords: Anaeromassilibacillus senegalensis; culturomics; genome; human gut; taxonogenomics.
Figures





References
-
- Lagier J.C., Armougom F., Million M., Hugon P., Pagnier I., Robert C. Microbial culturomics: paradigm shift in the human gut microbiome study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Pribram E. F. Deuticke; 1933. Klassifikation der schizomyceten (bakterien): Versuch einer wissenschaftlichen Klassifikation der bakterien auf botanischer grundlage.
-
- Cato E.P., George W.L., Finegold S.M. Genus Clostridium Prazmowski 1880, 23 AL. In: Sneath P.H.A., Mair N.S., Sharpe M.E., Holt J.G., editors. Vol. 2. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore, MD: 1986. pp. 1141–1200. (Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology).
-
- Vos P., Garrity G., Jones D., Krieg N.R., Ludwig W., Rainey F.A. Vol. 3. Springer Science & Business Media; Amsterdam: 2011. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. The Firmicutes.
-
- Rosselló-Mora R. DNA-DNA reassociation methods applied to microbial taxonomy and their critical evaluation. In: Stackebrandt E., editor. Molecular identification, systematics, and population structure of prokaryotes. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2006. pp. 23–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
