Bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn: A water-soluble and recycle catalyst for various organic transformations
- PMID: 28289549
- PMCID: PMC5338870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.12.005
Bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn: A water-soluble and recycle catalyst for various organic transformations
Abstract
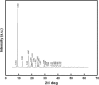
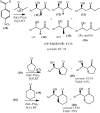
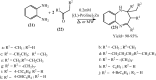
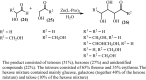
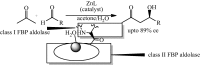
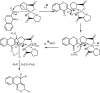
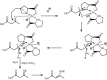
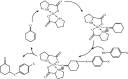
Under the green chemistry perspective, bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn (also called zinc-proline or Zn[(l)-pro]2) has proven its competence as a promising alternative in a plethora of applications such as catalyst or promoter. Owing to its biodegradable and non-toxic nature of bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn, it is being actively investigated as a water soluble green catalyst for synthetic chemistry. Bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn are readily utilized under mild conditions and have high selectivity and reactivity with broad range of substrate acceptance to make it better reaction medium for a wide variety of organic transformations. This Review summarizes the till date literature on its synthesis, characterization, and its catalytic role in various organic reactions.
Keywords: Amino-acid complex; Asymmetric catalyst; Bis[(l)prolinate-N,O]Zn; Lewis acid; Organometallic chemistry; Zinc.
Figures















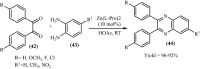
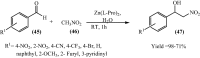

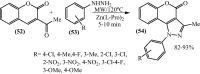

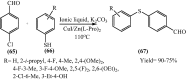










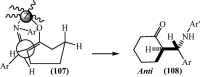

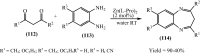







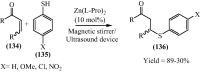




References
-
- Christiansons W.D., Lipscomb W.N. Carboxypeptidase A. Acc Chem Res. 1992;22:62–69.
-
- Caroline M.L., Kandasamy A., Mohan R., Vasudevan S. Growth and characterization of dichlorobis l-prolineZn(II): a semi organic nonlinear optical single crystal. J Crystal Growth. 2009;311:1161–1165.
-
- Aoki S., Kimura E. Zinc-nucleic acid interaction. Chem Rev. 2004;104:769–787. - PubMed
-
- Yukawa Y., Inomata Y., Takeuchi T., Ouchi M.A.S. The structure of dichloro(4-hydroxy-l-proline)cadmium (II) Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1982;55:3135–3137.
-
- Yukawa Y., Inomata Y., Takeuchi T. Structure and properties of dichloro(4-hydroxy-l-proline)cadmium (II) hydrate. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1983;56:2125–2128.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

