A novel intronic splice site tafazzin gene mutation detected prenatally in a family with Barth syndrome
- PMID: 28289596
- PMCID: PMC5343338
- DOI: 10.1515/bjmg-2016-0043
A novel intronic splice site tafazzin gene mutation detected prenatally in a family with Barth syndrome
Abstract
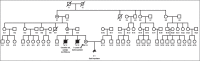
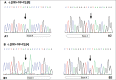
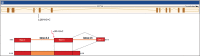
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is a rare X-linked disease characterized by dilated cardiomyopathy, proximal skeletal myopathy and cyclic neutropenia. It is caused by various mutations in the tafazzin (TAZ) gene located on Xq28 that results in remodeling of cardiolipin and abnormalities in mitochondria stability and energy production. Here we report on a novel c.285-1G>C splice site mutation in intron 3 of the TAZ gene that was detected prenatally.
Keywords: 3-Methylglutaconin aciduria; Barth Syndrome (BTHS); Neutropenia; Tafazzin (TAZ) gene; cardiomyopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Barth PG, Scholte HR, Berden JM, van der Klei-Van Moorsel JM, Luyt Houwen IE, van’t Veer Korthof ET. et al. An X-linked mitochondrial disease affecting cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and neutrophil leukocytes. J Neurol Sci 1983. 62(1-3):327–355. - PubMed
-
- Barth Syndrome Foundation Website: Frequently Asked Questions. 2006 http://www.barthsyndrome.org
-
- Kelley RI, Cheatham JP, Clark BJ, Nigro MA, Powell BR, Sherwood GW. et al. X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy with neutropenia, growth retardation, and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria. J Pediatr. 1991;119(5):738–747. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
