CT-guided versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma against the diaphragmatic dome
- PMID: 28291254
- PMCID: PMC5349557
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44583
CT-guided versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma against the diaphragmatic dome
Abstract
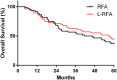
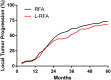
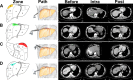
Computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation (CT-RFA) and laparoscopic RFA (L-RFA) have been used to treat intrahepatic recurrent small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) against the diaphragmatic dome. However, the therapeutic safety, efficacy, and hospital fee have never been compared between the two techniques due to scarcity of cases. In this retrospective study, 116 patients were divided into two groups with a total of 151 local recurrent HCC lesions abutting the diaphragm. We compared overall survival (OS), local tumor progression (LTP), postoperative complications, and hospital stay and fee between the two groups. Our findings revealed no significant differences in 5-year OS (36.7% vs. 44.6%, p = 0.4289) or 5-year LTP (73.3% vs. 67.9%, p = 0.8897) between CT-RFA and L-RFA. The overall hospital stay (2.8 days vs. 4.1 days, p < 0.0001) and cost (¥ 19217.6 vs. ¥ 25553.6, p < 0.0001) were significantly lower in the CT-RFA in comparison to that of L-RFA. In addition, we elaborated on the choice of percutaneous puncture paths depending on the locations of the HCC nodules and 11-year experience with CT-RFA. In conclusion, CT-RFA is a relatively easy and economic technique for recurrent small HCC abutting the diaphragm, and both CT-RFA and L-RFA are effective techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic vs computerized tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation for large hepatic hemangiomas abutting the diaphragm.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 21;21(19):5941-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i19.5941. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26019459 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography (CT)-guided versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: a single-institution comparison of morbidity rates and hospital costs.Surg Endosc. 2011 Apr;25(4):1088-95. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1322-5. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Surg Endosc. 2011. PMID: 20848143
-
Transpulmonary computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation of liver neoplasms abutting the diaphragm with multiple bipolar electrodes.Indian J Cancer. 2015 Dec;52 Suppl 2:e64-8. doi: 10.4103/0019-509X.172516. Indian J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26728677
-
Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: the value of artificial ascites.Abdom Imaging. 2009 May-Jun;34(3):371-80. doi: 10.1007/s00261-008-9408-4. Abdom Imaging. 2009. PMID: 18463915 Review.
-
Radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors.Eur Radiol. 2005 May;15(5):884-94. doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2652-x. Epub 2005 Mar 8. Eur Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15754165 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for subphrenic versus nonsubphrenic hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matched study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Dec;46(12):5735-5745. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03291-6. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 34581928
-
TACE sequential MWA guided by cone-beam computed tomography in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma under the hepatic dome.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 29;23(1):600. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11066-z. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37386361 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic thermoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis: an effective procedure for tricky tumors.Med Oncol. 2020 Mar 19;37(4):32. doi: 10.1007/s12032-020-1342-5. Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32193636
-
Overall Survival and Complication Rates in the Treatment of Liver Carcinoma: A Comparative Study of Ultrasound, Computed Tomography, and Combined Ultrasound and Computed Tomography Guidance for Radiofrequency Ablation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;15(14):1754. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15141754. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722504 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of Stereotactic Radiofrequency Ablation (SRFA) for Malignant Liver Tumors: Novice versus Experienced Operators.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 22;12(2):175. doi: 10.3390/biology12020175. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song I., Rhim H., Lim H. K., Kim Y.-s. & Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm and gastrointestinal tracts with the use of artificial ascites: safety and technical efficacy in 143 patients. European Radiology 19, 2630–2640, doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1463-x (2009). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim Y. K., Kim C. S., Lee J. M., Chung G. H. & Chon S. B. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome with the CT-guided extrathoracic transhepatic approach. European Journal of Radiology 60, 100–107, 10.1016/j.ejrad.2006.05.002 (2006). - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

