Effects of bumetanide on neurobehavioral function in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders
- PMID: 28291262
- PMCID: PMC5416661
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2017.10
Effects of bumetanide on neurobehavioral function in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders
Erratum in
-
Effects of bumetanide on neurobehavioral function in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 May 9;7(5):e1124. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.101. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28485727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
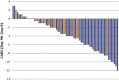
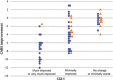
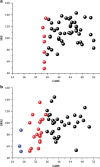
In animal models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), the NKCC1 chloride-importer inhibitor bumetanide restores physiological (Cl-)i levels, enhances GABAergic inhibition and attenuates electrical and behavioral symptoms of ASD. In an earlier phase 2 trial; bumetanide reduced the severity of ASD in children and adolescents (3-11 years old). Here we report the results of a multicenter phase 2B study primarily to assess dose/response and safety effects of bumetanide. Efficacy outcome measures included the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), the Social Responsive Scale (SRS) and the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Improvement scale (CGI-I). Eighty-eight patients with ASD spanning across the entire pediatric population (2-18 years old) were subdivided in four age groups and randomized to receive bumetanide (0.5, 1.0 or 2.0 mg twice daily) or placebo for 3 months. The mean CARS value was significantly improved in the completers group (P: 0.015). Also, 23 treated children had more than a six-point improvement in the CARS compared with only one placebo-treated individual. Bumetanide significantly improved CGI (P: 0.0043) and the SRS score by more than 10 points (P: 0.02). The most frequent adverse events were hypokalemia, increased urine elimination, loss of appetite, dehydration and asthenia. Hypokalemia occurred mainly at the beginning of the treatment at 1.0 and 2.0 mg twice-daily doses and improved gradually with oral potassium supplements. The frequency and incidence of adverse event were directly correlated with the dose of bumetanide. Therefore, bumetanide improves the core symptoms of ASD and presents a favorable benefit/risk ratio particularly at 1.0 mg twice daily.
Conflict of interest statement
The study was sponsored by Neurochlore, a biotech company dedicated to the development of novel therapies to autism and other developmental disorders. EL, DR and YB-A are founders and shareholders of the company. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest. Funding of the trial comes from an investment of Symmetry Capital, a grant from France's Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-12-RPIB-0001-01) and French Government loans. We are grateful to the Bettencourt-Schuller foundation for support of the experimental investigations on ASD.
Figures
References
-
- Ben-Ari Y. The GABA excitatory/inhibitory developmental sequence: a personal journey. Neuroscience 2014; 279C: 187–219. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3: 728–739. - PubMed
-
- Boulenguez P, Liabeuf S, Bos R, Bras H, Jean-Xavier C, Brocard C et al. Down-regulation of the potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC2 contributes to spasticity after spinal cord injury. Nat Med 2010; 16: 302–307. - PubMed
-
- Cohen I. On the origin of interictal activity in human temporal lobe epilepsy in vitro. Science 2002; 298: 1418–1421. - PubMed
-
- Nardou R, Yamamoto S, Chazal G, Bhar A, Ferrand N, Dulac O et al. Neuronal chloride accumulation and excitatory GABA underlie aggravation of neonatal epileptiform activities by phenobarbital. Brain 2011; 134(Pt 4): 987–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

