Systolic-diastolic hypertension versus isolated systolic hypertension and incident heart failure in older adults: Insights from the Cardiovascular Health Study
- PMID: 28291625
- PMCID: PMC6454896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.02.139
Systolic-diastolic hypertension versus isolated systolic hypertension and incident heart failure in older adults: Insights from the Cardiovascular Health Study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Systolic-diastolic hypertension versus isolated systolic hypertension and incident heart failure in older adults: Insights from the cardiovascular health study" [Int. J. Cardiol. 235 (2017) 11-16].Int J Cardiol. 2017 Jul 1;238:181. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.04.072. Epub 2017 May 6. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28487149 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) is common in older adults and is a risk factor for incident heart failure (HF). We examined the association of systolic-diastolic hypertension (SDH) with incident HF and other outcomes in older adults.
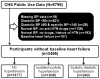
Methods: In the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS), 5776 community-dwelling adults≥65years had data on baseline systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP). We excluded those with DBP<60mmHg (n=821), DBP≥90 and SBP<140mmHg (n=28), normal BP, taking anti-hypertensive drugs (n=1138), normal BP, not taking anti-hypertensive drugs, history of hypertension (n=193), and baseline HF (n=101). Of the remaining 3495, 1838 had ISH (SBP≥140 and DBP<90mmHg) and 240 had SDH (SBP≥140 and DBP≥90mmHg). The main outcome was centrally-adjudicated incident HF over 13years of follow-up.
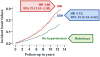
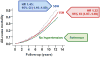
Results: Participants had a mean (±SD) age of 73 (±6)years, 57% were women, and 16% African American. Incident HF occurred in 25%, 22% and 11% of participants with ISH, SDH and no hypertension, respectively. Compared to no hypertension, multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for incident HF associated with ISH and SDH were 1.86 (1.51-2.30) and 1.73 (1.23-2.42), respectively. Cardiovascular mortality occurred in 22%, 24% and 9% of those with ISH, SDH and no hypertension, respectively with respective multivariable-adjusted HRs (95% CIs) of 1.88 (1.49-2.37) and 2.30 (1.64-3.24).
Conclusion: Among older adults with hypertension, both SDH and ISH have similar associations with incident HF and cardiovascular mortality.
Keywords: Incident heart failure; Isolated diastolic hypertension; Mortality; Systolic–diastolic hypertension.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Assessment of isolated systolic hypertension with lower diastolic and the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Sep 1;242:20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.143. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28619323 No abstract available.
-
Treatment of systolic hypertension and low diastolic blood pressure in older adults: How low is too low?!Int J Cardiol. 2017 Sep 1;242:21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.04.096. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28619324 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fried LP, Borhani NO, Enright P, et al. The Cardiovascular Health Study: design and rationale. Ann Epidemiol. 1991;1:263–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

