Proteolysis of truncated hemolysin A yields a stable dimerization interface
- PMID: 28291749
- PMCID: PMC5349307
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X17002102
Proteolysis of truncated hemolysin A yields a stable dimerization interface
Abstract
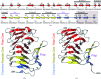
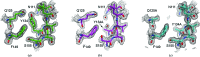
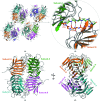
Wild-type and variant forms of HpmA265 (truncated hemolysin A) from Proteus mirabilis reveal a right-handed, parallel β-helix capped and flanked by segments of antiparallel β-strands. The low-salt crystal structures form a dimeric structure via the implementation of on-edge main-chain hydrogen bonds donated by residues 243-263 of adjacent monomers. Surprisingly, in the high-salt structures of two variants, Y134A and Q125A-Y134A, a new dimeric interface is formed via main-chain hydrogen bonds donated by residues 203-215 of adjacent monomers, and a previously unobserved tetramer is formed. In addition, an eight-stranded antiparallel β-sheet is formed from the flap regions of crystallographically related monomers in the high-salt structures. This new interface is possible owing to additional proteolysis of these variants after Tyr240. The interface formed in the high-salt crystal forms of hemolysin A variants may mimic the on-edge β-strand positioning used in template-assisted hemolytic activity.
Keywords: Proteus mirabilis; alternate crystal forms; hemolysin A; proteolysis; two-partner secretion; β-helix.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

