Gentle, fast and effective crystal soaking by acoustic dispensing
- PMID: 28291760
- PMCID: PMC5349437
- DOI: 10.1107/S205979831700331X
Gentle, fast and effective crystal soaking by acoustic dispensing
Abstract
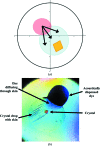
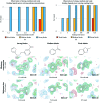
The steady expansion in the capacity of modern beamlines for high-throughput data collection, enabled by increasing X-ray brightness, capacity of robotics and detector speeds, has pushed the bottleneck upstream towards sample preparation. Even in ligand-binding studies using crystal soaking, the experiment best able to exploit beamline capacity, a primary limitation is the need for gentle and nontrivial soaking regimens such as stepwise concentration increases, even for robust and well characterized crystals. Here, the use of acoustic droplet ejection for the soaking of protein crystals with small molecules is described, and it is shown that it is both gentle on crystals and allows very high throughput, with 1000 unique soaks easily performed in under 10 min. In addition to having very low compound consumption (tens of nanolitres per sample), the positional precision of acoustic droplet ejection enables the targeted placement of the compound/solvent away from crystals and towards drop edges, allowing gradual diffusion of solvent across the drop. This ensures both an improvement in the reproducibility of X-ray diffraction and increased solvent tolerance of the crystals, thus enabling higher effective compound-soaking concentrations. The technique is detailed here with examples from the protein target JMJD2D, a histone lysine demethylase with roles in cancer and the focus of active structure-based drug-design efforts.
Keywords: Diamond Light Source I04-1; Structural Genomics Consortium; XChem; acoustic droplet ejection; crystal soaking; fragment screening.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

