Comprehensive molecular exploration identified promoter DNA methylation of the CRBP1 gene as a determinant of radiation sensitivity in rectal cancer
- PMID: 28291773
- PMCID: PMC5396119
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.65
Comprehensive molecular exploration identified promoter DNA methylation of the CRBP1 gene as a determinant of radiation sensitivity in rectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) for advanced rectal cancer (RC) is a well-evidenced therapy; however, some RC patients have no therapeutic response. Patient selection for NCRT so that non-responsive patients are excluded has been subjective. To date, no molecular markers indicating radiation sensitivity have been reported.
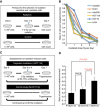
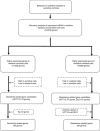
Methods: We irradiated six colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines and identified HCT116 cells as radiation-sensitive and HCT15 and DLD-1 cells as radiation resistant. Using a microarray, we selected candidate radiation sensitivity marker genes by choosing genes whose expression was consistent with a radiation-resistant or sensitive cell phenotype.
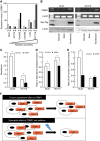
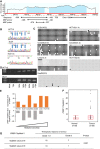
Results: Among candidate genes, cellular retinol binding protein 1 (CRBP1) was of particular interest because it was not only induced in HCT116 cells by tentative 10 Gy radiation treatments, but also its expression was increased in HCT116-derived radiation-resistant cells vs parental cells. Forced expression of CRBP1 decreased the viability of both HCT15 and DLD-1 cells in response to radiation therapy. We also confirmed that CRBP1 was epigenetically silenced by hypermethylation of its promoter DNA, and that the quantitative methylation value of CRBP1 significantly correlated with histological response in RC patients with NCRT (P=0.031).
Conclusions: Our study identified CRBP1 as a radiation-sensitive predictor in RC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyoshi T, Kobunai T, Watanabe T (2012) Predicting the response to preoperative radiation or chemoradiation by a microarray analysis of the gene expression profiles in rectal cancer. Surg Today 42: 713–719. - PubMed
-
- Arigami T, Uenosono Y, Ishigami S, Yanagita S, Hagihara T, Haraguchi N, Matsushita D, Hirahara T, Okumura H, Uchikado Y, Nakajo A, Hokita S, Natsugoe S (2013) Clinical significance of stanniocalcin 2 expression as a predictor of tumor progression in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 30: 2838–2844. - PubMed
-
- Chang AC-M, Jellinek DA, Reddel RR (2003) Mammalian stanniocalcins and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 10: 359–373. - PubMed
-
- Ebert MPA, Tänzer M, Balluff B, Burgermeister E, Kretzschmar AK, Hughes DJ, Tetzner R, Lofton-Day C, Rosenberg R, Reinacher-Schick AC, Schulmann K, Tannapfel A, Hofheinz R, Röcken C, Keller G, Langer R, Specht K, Porschen R, Stöhlmacher-Williams J, Schuster T, Ströbel P, Schmid RM (2012) TFAP2E-DKK4 and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 366: 44–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

