Purification of cone outer segment for proteomic analysis on its membrane proteins in carp retina
- PMID: 28291804
- PMCID: PMC5349680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173908
Purification of cone outer segment for proteomic analysis on its membrane proteins in carp retina
Abstract
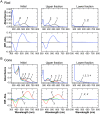
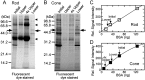
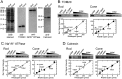
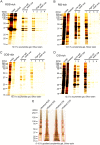
Rods and cones are both photoreceptors in the retina, but they are different in many aspects including the light response characteristics and, for example, cell morphology and metabolism. These differences would be caused by differences in proteins expressed in rods and cones. To understand the molecular bases of these differences between rods and cones, one of the ways is to compare proteins expressed in rods and cones, and to find those expressed specifically or dominantly. In the present study, we are interested in proteins in the outer segment (OS), the site responsible for generation of rod- or cone-characteristic light responses and also the site showing different morphology between rods and cones. For this, we established a method to purify the OS and the inner segment (IS) of rods and also of cones from purified carp rods and cones, respectively, using sucrose density gradient. In particular, we were interested in proteins tightly bound to the membranes of cone OS. To identify these proteins, we analyzed proteins in some selected regions of an SDS-gel of washed membranes of the OS and the IS obtained from both rods and cones, with Liquid Chromatography-tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) using a protein database constructed from carp retina. By comparing the lists of the proteins found in the OS and the IS of both rods and cones, we found some proteins present in cone OS membranes specifically or dominantly, in addition to the proteins already known to be present specifically in cone OS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of NDRG1 family proteins on photoreceptor outer segment morphology in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 4;6:36590. doi: 10.1038/srep36590. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27811999 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-independent suppression of light-activated visual pigment by arrestin in carp rods and cones.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9399-411. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.634543. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713141 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of cone molecular markers in rhodopsin-mutant human retinas with retinitis pigmentosa.Mol Vis. 2000 Nov 3;6:204-15. Mol Vis. 2000. PMID: 11063754
-
Molecular bases of rod and cone differences.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Sep;90:101040. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101040. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34974196 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms characterizing cone photoresponses.Photochem Photobiol. 2007 Jan-Feb;83(1):19-26. doi: 10.1562/2006-02-28-IR-823. Photochem Photobiol. 2007. PMID: 16706600 Review.
Cited by
-
Phototransduction in retinal cones: Analysis of parameter importance.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 28;16(10):e0258721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258721. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34710119 Free PMC article.
-
Function of animal rhodopsins and related proteins: Report for the session 9.Biophys Physicobiol. 2023 Mar 2;20(Supplemental):e201018. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v20.s018. eCollection 2023 Mar 21. Biophys Physicobiol. 2023. PMID: 38362327 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structural Impact of Selected Retinoids on Model Photoreceptor Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Jun 1;13(6):575. doi: 10.3390/membranes13060575. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pugh EN Jr. Lamb TD. Amplification and kinetics of the activation steps in phototransduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993; 1141(2–3):111–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

