Identification of cerebral perfusion using arterial spin labeling in patients with seizures in acute settings
- PMID: 28291816
- PMCID: PMC5349669
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173538
Identification of cerebral perfusion using arterial spin labeling in patients with seizures in acute settings
Abstract
This study aimed to explore the utility of arterial spin labeling perfusion-weighted imaging (ASL-PWI) in patients with suspected seizures in acute settings. A total of 164 patients who underwent ASL-PWI for suspected seizures in acute settings (with final diagnoses of seizure [n = 129], poststroke seizure [n = 18], and seizure mimickers [n = 17]), were included in this retrospective study. Perfusion abnormality was analyzed for: (1) pattern, (2) multifocality, and (3) atypical distribution against vascular territories. Perfusion abnormality was detected in 39% (50/129) of the seizure patients, most (94%, 47/50) being the hyperperfusion pattern. Of the patients with perfusion abnormality, multifocality or hemispheric involvement and atypical distribution against vascular territory were revealed in 46% (23/50) and 98% (49/50), respectively. In addition, seizures showed characteristic features including hyperperfusion (with or without non-territorial distribution) on ASL-PWI, thus differentiating them from poststroke seizures or seizure mimickers. In patients in whom seizure focus could be localized on both EEG and ASL-PWI, the concordance rate was 77%. The present study demonstrates that ASL-PWI can provide information regarding cerebral perfusion status in patients with seizures in acute settings and has the potential to be used as a non-invasive imaging tool to identify the cerebral perfusion in patients with seizures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
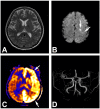
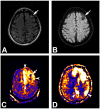
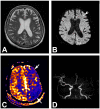
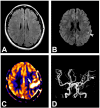
References
-
- Alsop DC, Connelly A, Duncan JS, Hufnagel A, Pierpaoli C, Rugg-Gunn FJ. Diffusion and perfusion MRI in epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2002;43:69–77.
-
- Wilder-Smith E, Nirkko AC. Contribution of concurrent Doppler and EEG in differentiating occipital epileptic discharges from migraine. Neurology. 1991;41(12):2005–7. Epub 1991/12/01. - PubMed
-
- Duncan R. Epilepsy, cerebral blood flow, and cerebral metabolic rate. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1992;4(2):105–21. Epub 1992/01/01. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

